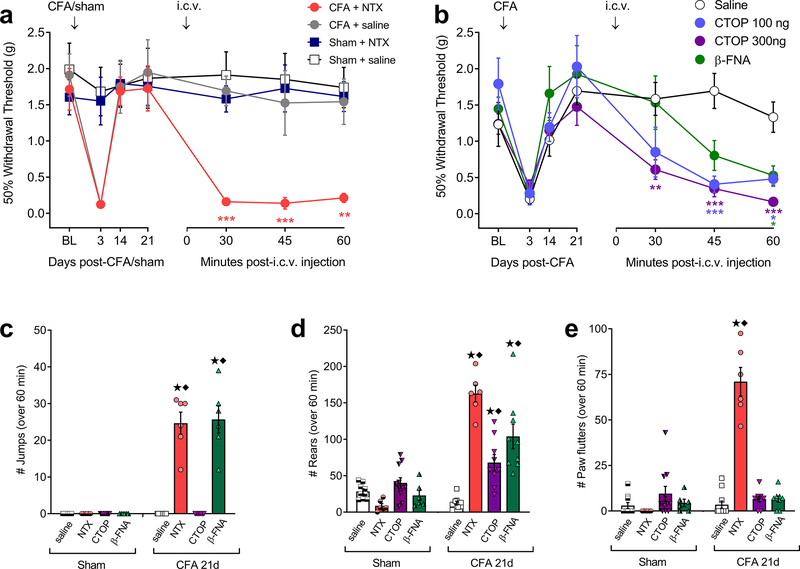
Figure 1. Intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of opioid receptor inverse agonists reinstated mechanical hyperalgesia and induced withdrawal behaviors.
(a) Effect of i.c.v. injection of naltrexone (NTX; 1 μg) or saline on mechanical thresholds in male mice, tested 21 days after intra-plantar injection of CFA or saline (sham) (2-way RM ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests; n = 6; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001 compared to sham + saline). (b) Effect of i.c.v. injection of the MOR-selective inverse agonists CTOP (100 and 300 ng), β-FNA (1 μg) or saline on mechanical thresholds in mice 21 days after CFA (n = 7 – 14; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 compared to saline). (c to e) Incidence of i.c.v. inverse agonist-induced withdrawal behaviors including (c) jumping, (d) rearing, and (e) paw flutters. ★ P < 0.05 compared to Sham + the respective antagonist. ◆ P < 0.05 compared to CFA-21d + saline. All data shown as mean ± S.E.M.