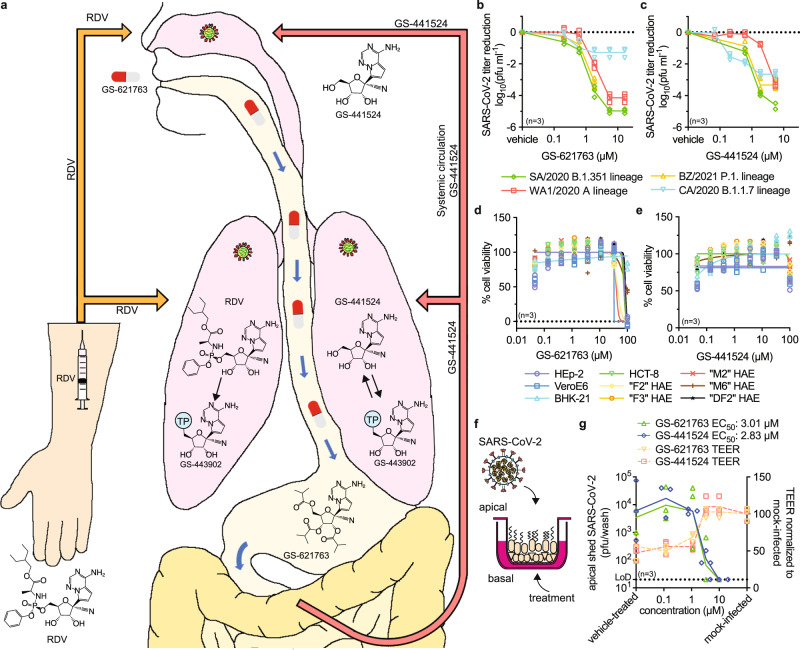
Fig. 1. Antiviral potency of remdesivir analog GS-621763.
a Schematic depicting metabolism of remdesivir (RDV; orange arrows) and GS-621763 (red/white pills; red arrows) after injection or oral uptake, respectively. Remdesivir distributes into tissues (e.g., lung) and is efficiently metabolized intracellularly to GS-443902 (TP = triphosphate). Conversely, GS-441524 is the dominant plasma metabolite after intestinal absorption of orally administered GS-627163 and is subsequently anabolized to GS-443902 in the tissues. b–c Virus yield reduction of SARS-CoV-2 clinical isolates WA1/2020 (red squares), CA/2020 (blue triangles), SA/2020 (green diamonds), and BZ/2021 (yellow triangles) representing the A, B.1.1.7 (α), B.1.351 (β) and P.1 (γ) lineages, respectively, by GS-621763 (b) and GS-441524 (c) on VeroE6 cells. EC50 concentrations are specified in Supplementary Table 1. d–e In vitro cytotoxicity profiles of GS-621763 (d) and GS-441524 (e) on VeroE6 (blue squares), HEp-2 (purple circles), BHK-21 (light blue triangles), HCT-8 (green triangles) and a panel of primary HAE cells from independent donors (“F2” (yellow diamonds), “F3” (orange circles), “M2” (red “×” symbols), “M6” (brown “+” symbols), “DF2” (black stars)). f schematic of well-differentiated air-liquid interface HAE cultures. g HAEs were infected from the apical side with SARS-CoV-2 VOC γ and treated from the basolateral side with GS-621763 or GS-441524. Apically shed virus titers (green triangles and blue diamonds for GS-621763 or GS-441524, respectively) on day after infection and the impact of treatment on preserving tissue integrity (transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) (orange triangles and red squares for GS-621763 or GS-441524, respectively) are shown. LoD, the limit of detection. In (b–e, g), symbols represent individual biological repeats (n = 3), lines (b–c, g) intersect the mean, lines in (d–e) depict nonlinear regression models.