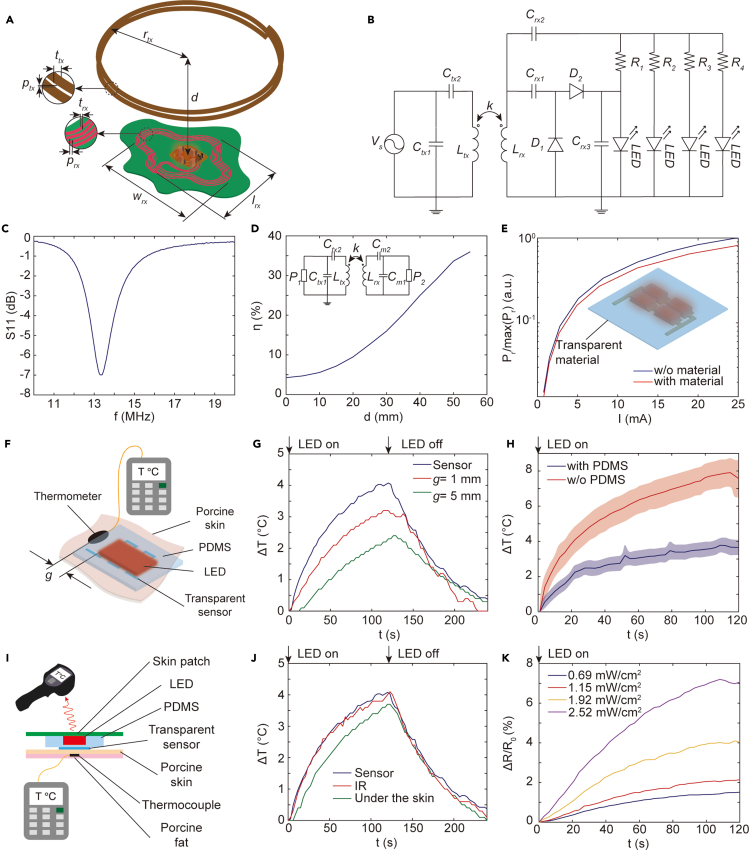
Figure 3.
Design and performance of the wireless system
(A) System design parameters.
(B) Circuit diagram of the wireless transmitter (left) and optoelectronic patch (right).
(C) Reflection coefficient S11 of the optimized circuit measure from the load. The operating frequency is 13.56 MHz.
(D) Power transfer efficiency η as a function of the distance d between transmitter and device for Cm1=737 pF and Cm2=80 pF.
(E) Measured optical radiant power as a function of current I in the LED array with and without the transparent sensor.
(F) Illustration of the experimental setup using an adjacent thermocouple.
(G) Thermal monitoring comparison with a distant thermocouple. g is the distance between the thermocouple and LED array using setup in (F).
(H) Temperature change measured by the transparent sensor with and without thermal insulation (PDMS) using setup in (F). Graphs show mean and SD (n = 3 technical trials).
(I) Illustration of the experimental setup using infrared camera and subdermal thermocouple.
(J) Thermal monitoring comparison with an infrared (IR) sensor and a subdermal thermocouple using the setup in (I).
(K) Relative change in resistance of the transparent sensor when illuminating porcine skin at different power densities.