Figure 3. Key Physiological and Laboratory Parameters at Baseline and 24 Hours That Differed Between Patients With Large Follow-up Infarct Volume and Discrepant Modified Rankin Scale Scores vs Nondiscrepant Modified Rankin Scale Scores .
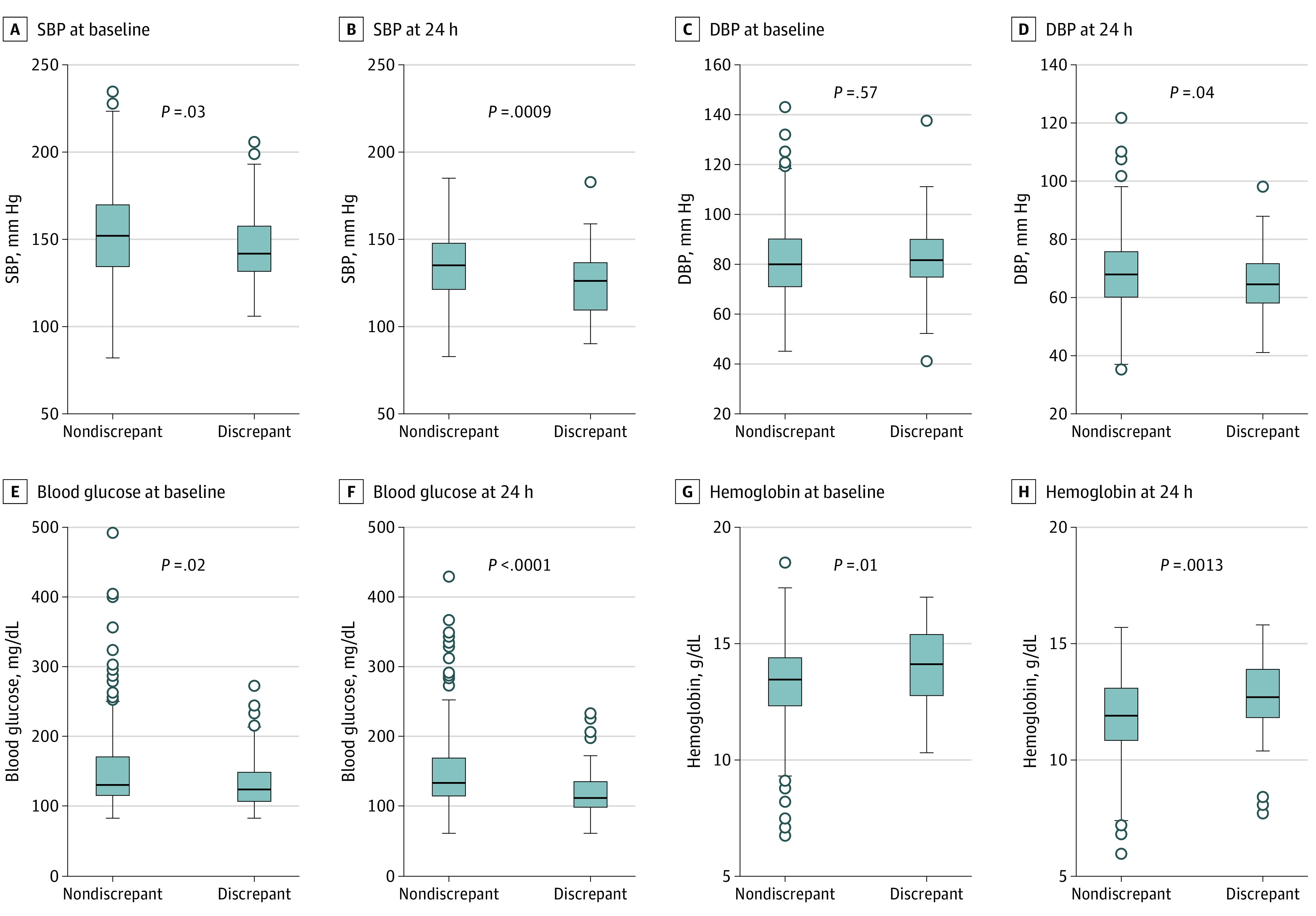
Discrepant cases, who had good outcome (ie, modified Rankin Scale score, ≤2) despite large follow-up infarct volume (ie, ≥92 mL), had significantly lower systolic blood pressure (SBP) and glucose levels and higher hemoglobin levels at 24 hours vs patients who had large FIV and poor outcome (ie, modified Rankin Scale score ≥3), even after applying the Hochberg correction (significance threshold of .0013). P values are from the Wilcoxon rank-sum test comparing discrepant with nondiscrepant cases. DBP indicates diastolic blood pressure. To convert glucose to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.0555; hemoglobin to grams per liter, multiply by 10.
