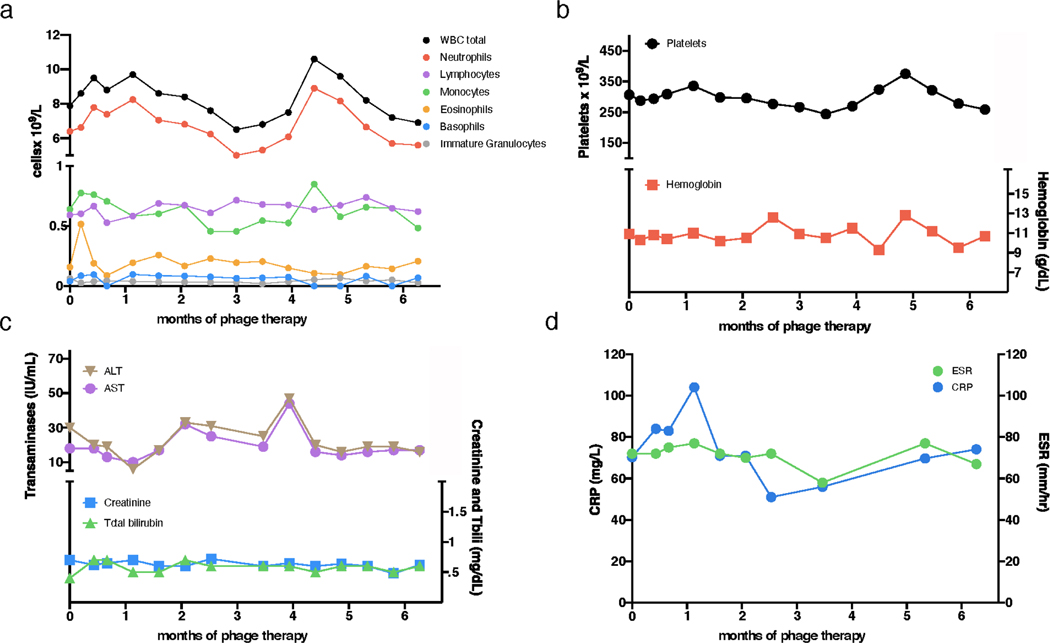
Extended Data Figure 4. Clinical indicators during phage treatment.
Safety assessments during phage treatment included regular monitoring of complete blood counts with differential, comprehensive metabolic panels, and inflammatory markers. During six-months of intravenous phage treatment there were no clinically significant differences observed in a, white blood cell (WBC) total counts and differentials, b, hemoglobin and platelets, c, liver function (alanine transaminase, ALT; aspartate transaminase, AST; and total bilirubin) or kidney function (creatinine), and d, C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).