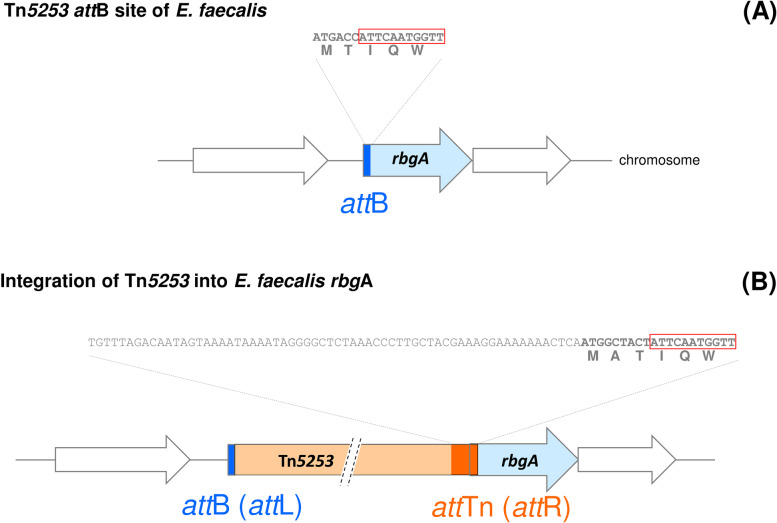
Fig. 3.
Tn5253 attB site and integration in E. faecalis chromosome. (A) Tn5253 attB (represented as a blue box) in E. faecalis is composed by 17 nucleotides which correspond to the first 17 nucleotides of the rbgA CDS (light blue arrow). In streptococci and enterococci, Tn5253 always integrates downstream of a conserved 11-nucleotides sequence (boxed in red). The nucleotide sequence of attB and deduced amino acid sequence are reported. (B) Site specific integration of Tn5253 into rbgA causes integration site duplication, restoring an intact CDS. The integration of Tn5253 into bacterial chromosome seems to be polarized, since attTn (orange box) always flanks the element (light orange box) at the right end. In E. faecalis integration site duplication results in the acquisition of an additional codon (GCT ◊ Alanine) in the rbgA CDS. attB and attTn sites are not scaled. The 84 nucleotides sequence of attTn and the deduced amino acid sequence of RbgA N-terminal end are reported. Amino acids single-letter code is used