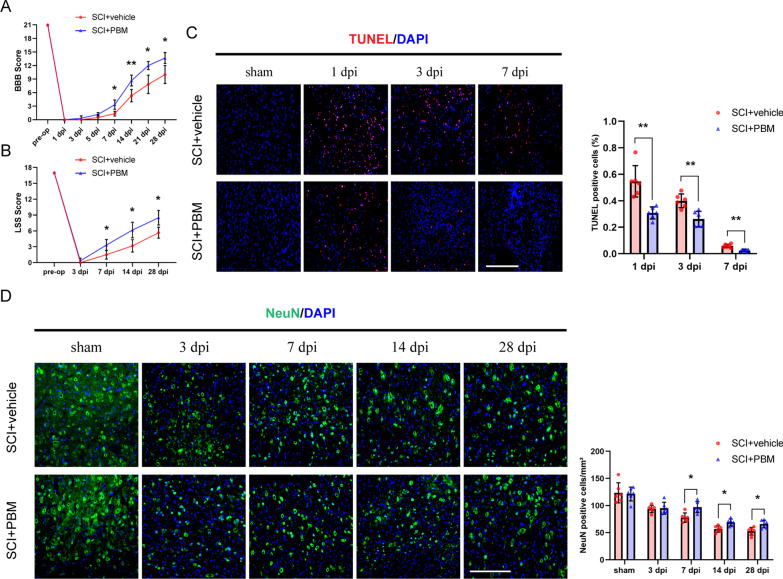
Fig. 1.
PBM promoted the recovery of motor function, reduced tissue apoptosis, and increased the number of surviving neurons after SCI. A, B The BBB score and LSS were used to evaluate the recovery of motor function in the SCI + vehicle group and the SCI + PBM group (n = 6 rats per group). C TUNEL staining was used to detect the level of apoptosis in injured spinal cord tissue at 1 dpi, 3 dpi and 7 dpi. dpi: days post-injury. Representative images were obtained within ± 150 μm of the lesion epicenter in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. The apoptotic rate is represented by the number of TUNEL+ cells divided by the total number of cells in which nuclei were labeled in each field. Quantification of the TUNEL+ cell rate in the SCI + vehicle group and the SCI + PBM group (n = 6 rats per group at each time point). D The number of surviving neurons in the ventral spinal cord gradually decreased within 28 dpi. Representative images were obtained within ± 150 μm of the lesion epicenter in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. Quantification of the number of NeuN+ cells in the SCI + vehicle group and the SCI + PBM group (n = 6 rats per group at each time point). Statistical comparisons were performed using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01