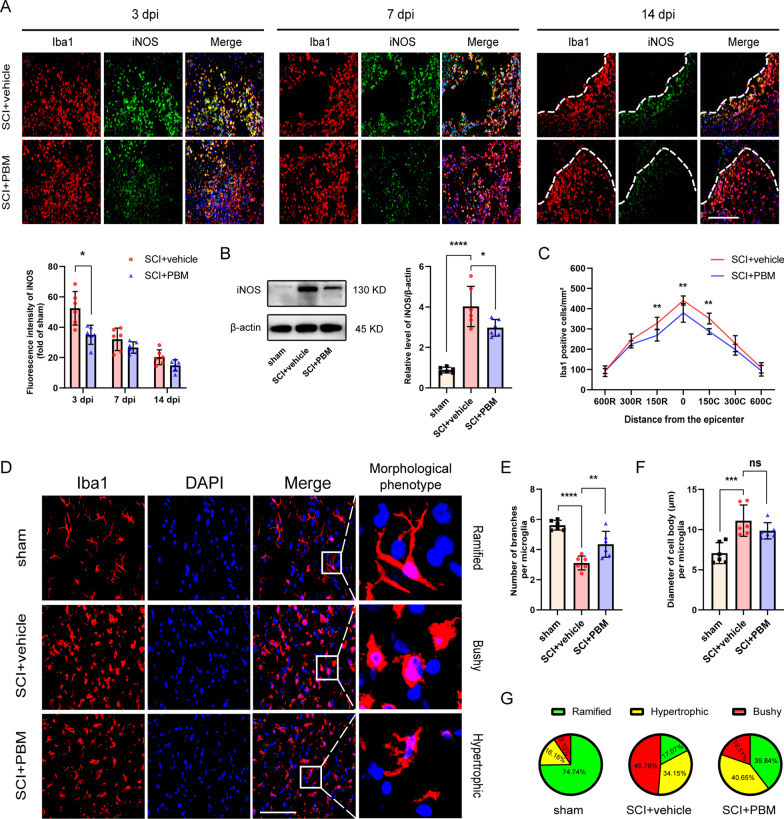
Fig. 3.
PBM inhibited the activation of neurotoxic microglia/macrophages after SCI. A Representative images of immunofluorescence staining for Iba1 (red) and iNOS (green) in from the lesion epicenter at 3 dpi, 7 dpi, and 14 dpi. Quantification of the intensity of iNOS relative to that in the sham control group (n = 6 rats per group at each time point). Statistical comparisons were performed using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. B Representative blots and quantification showing the expression level of iNOS in the injured spinal cord at 3 dpi (n = 6 rats per group). Statistical comparisons were performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. C Quantification of Iba1+ cells at different distances from the epicenter from rostral to caudal (600 μm, 300 μm, and 150 μm; n = 6 rats per group). Statistical comparisons were performed using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. D Representative images of Iba1+ cells at 150 μm from the epicenter in each group at 3 dpi. Microglia/macrophages were classified into ramified, bushy and hypertrophic phenotypes based on cellular morphological features. E, F Iba1+ cell morphology was assessed by the number of branches per cell and the diameter of the cell body per cell (n = 6 rats per group). Statistical comparisons were performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. G Representative percentages of ramified, hypertrophic and bushy microglial phenotypes in each group at 3 dpi. Scale bar: 200 μm. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns = nonsignificant