FIGURE 1.
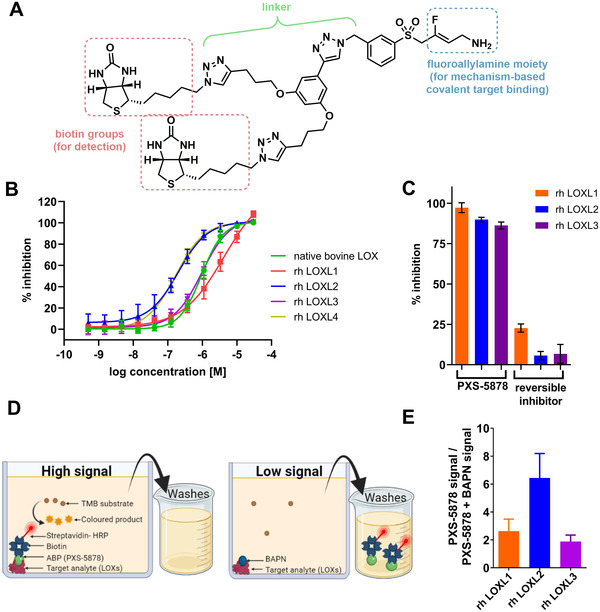
Characteristics of the activity‐based probe (ABP) PXS‐5878. (A) Chemical structure of PXS‐5878, with functional subunits denoted with different colours. The fluoroallylamine moiety (blue) was designed to interact with the lysine tyrosylquinone (LTQ) co‐factor within the lysyl oxidase active sites. An extended linker (green) was incorporated to provide optimal separation between the reactive functional group and the tag, avoiding unfavourable steric hindrance. Biotin was selected as a tag, with higher sensitivity found to be achieved using a double tag (red), resulting in PXS‐5878 as the preferred ABP. (B) Concentration‐dependent inhibition of recombinant human (rh) lysyl oxidase‐like 1‐4 (LOXL1‐4) and native bovine LOX in a standard Amplex Red assay with 30 min pre‐incubation; n = 3–4 independent experiments, standard error of mean (SEM). Native bovine LOX was used as a surrogate for human LOX as both enzymes have similar pharmacology for fluoroallylamines. 2 , 9 (C) Irreversible nature of PXS‐5878 enzyme inhibition confirmed using a jump dilution assay. Enzyme (rh LOXL1, rh LOXL2 or LOXL3) was pre‐incubated with 10 × IC50 of PXS‐5878 for 30 min, then diluted 100x and remaining activity assessed by Amplex Red assay. Little to no recovery in enzyme activity was seen for PXS‐5878. In contrast, enzyme activity almost fully recovered upon inhibition by an analogue of comparable potency but lacking the fluoro group (reversible inhibitor, Figure S1), confirming the importance of the putative leaving group for the irreversible binding profile. Each value is an average of three experiments. (D) Schematic representation of the assay development to detect lysyl oxidase activity by PXS‐5878 using a direct enzyme‐linked assay with lysyl oxidases as the target analyte. HRP: horseradish peroxidase; TMB: 3,3′,5,5′‐tetramethylbenzidine, a chromogenic substrate. After target analyte is bound to the plate, PXS‐5878 was incubated for 60 min in the presence or absence of a pan‐LOX inhibitor (β‐aminopropionitrile, [BAPN]) and streptavidin‐HRP is then added. After incubation the plate is washed and TMB added to measure the amount of bound ABP/streptavidin/HRP. This leads to a high signal. Application of BAPN to block the enzymatic site prevents PXS‐5878 from binding, and it is consequently washed off the plate, resulting in a low signal. In the final Simoa® assay, the enzyme is bound by the antibody to the bead. (E) Detection of enzymatically active lysyl oxidases by PXS‐5878. rh LOXL1, LOXL2 or LOXL3 were immobilised on the surface of a microtiter plate and processed as described in (D). Optical density in the absence of the pan‐LOX inhibitor BAPN (high signal) was divided by the value in the presence of BAPN (low signal). Low signal was 1.81 ± 0.77 (n = 8) times larger than blank controls. Two independent replicates were performed (total n = 4–5 for each enzyme).
