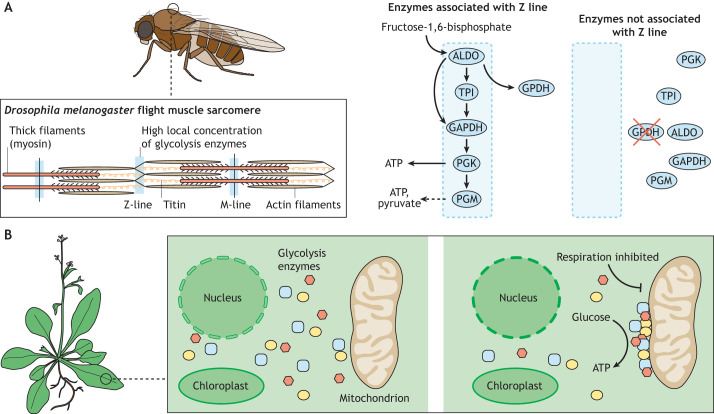
Fig. 6.
Non-condensate compartmentalization in plants and insects. (A) Colocalization of glycolysis enzymes in D. melanogaster flight muscle fibers. M-lines and Z-lines associate with glycolysis enzymes (indicated with blue). Glycolysis enzymes associated with Z-lines are shown on the right. In the presence of GPDH, multiple sequential glycolysis enzymes associate with the Z-line, allowing them to convert fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to ATP and pyruvate. Deletion of muscle GPDH disrupts localization of the other glycolysis enzymes, resulting in flight defects. (B) Substrate channeling on the mitochondrial membrane in plants. In Arabidopsis thaliana, glycolysis enzymes (yellow, blue and purple shapes) are diffusely localized in the cytosol. Inhibition of respiration triggers the accumulation of each glycolysis enzyme on mitochondrial membranes. These complexes promote substrate channeling through the glycolytic pathway, efficiently converting glucose into usable ATP.