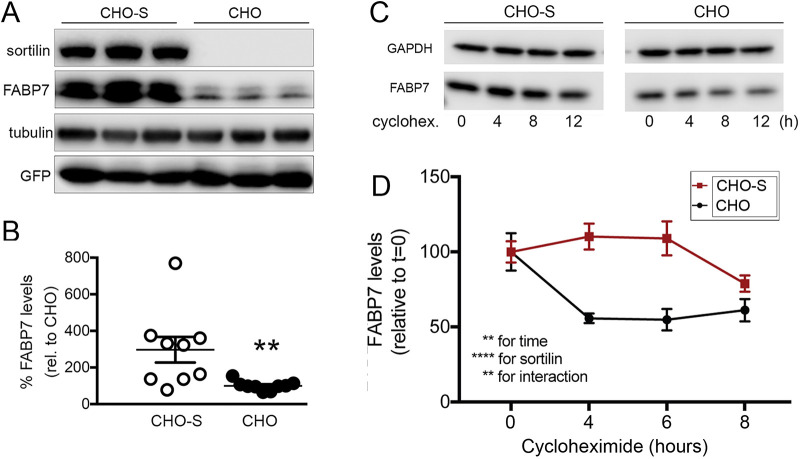
Fig. 3.
Sortilin stabilizes cellular levels of FABP7 in CHO cells. (A,B) Parental Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells or CHO cells stably expressing sortilin (CHO-S) were transiently transfected with expression constructs encoding for FABP7 and GFP. A representative western blot of documenting expression of sortilin and FABP7 in replicate lysates of CHO and CHO-S cells is shown in A. Detection of GFP and tubulin served as transfection and loading controls, respectively. B shows FABP7 levels in CHO and CHO-S transfectants as determined by densitometric scanning of replicate western blots (n=9 replicates from 3 independent experiments per cell line). Data are mean±s.e.m. given as percentage of FABP7 levels in CHO cells (set to 100%). Levels of FABP7 (but not of GFP) are significantly increased by the presence of sortilin in CHO-S compared with CHO cells. **P<0.01 (unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test). (C,D) CHO and CHO-S cells were transiently transfected with a FABP7-myc expression construct. At 48 h post transfection, replicate cultures of transfected cells were treated with 10 µg/ml of cycloheximide and collected at time points 0, 4, 8, and 12 h later. Levels of FABP7 were determined by western blotting (C). Detection of GAPDH served as loading control. The decrease in FABP7 levels was significantly faster in CHO than in CHO-S cells as determined by densitometric scanning of replicate blots (D; n=9 replicates per condition from three independent experiments). Data are mean±s.e.m. given as percentage of FABP7 levels in CHO or CHO-S at 0 h of treatment (set to 100%). **P<0.01; ****P<0.0001 (two-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni post-hoc analysis).