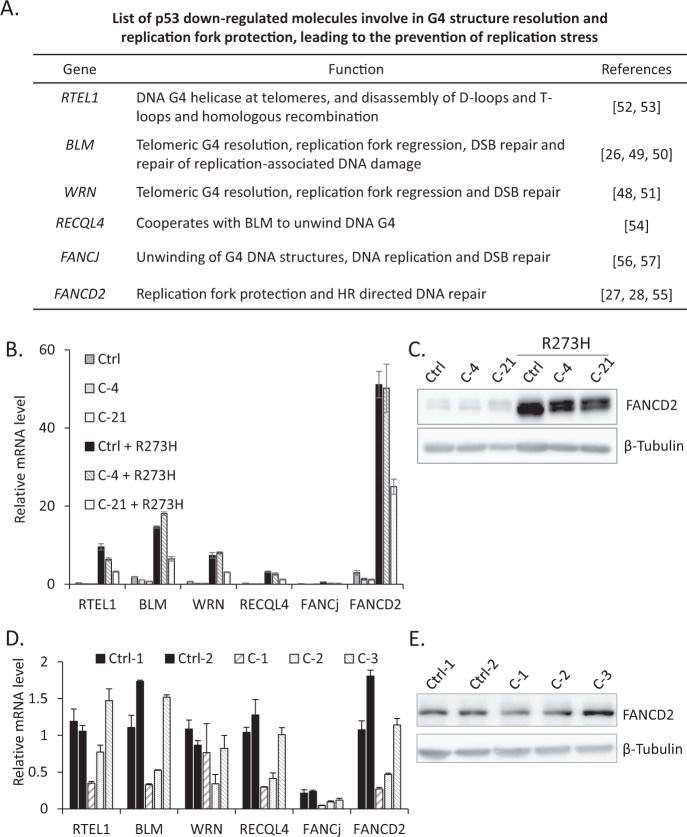
Fig. 5. p53 inactivation leads to the upregulation of G4-resolving helicases and FA pathway proteins involved in replication fork protection.
A List of p53 downregulated G4-resolving eukaryotic helicases or FA pathway DNA repair molecules and their proposed biological functions during DNA replication. B A comparison of TP53 wt and p53-inactivated Ctrl or ATRX KO cells suggested the p53-dependent regulation of G4-resolving helicases and the FA pathway DNA repair molecule, FANCD2. Real-time RT-PCR analysis of RTEL1, BLM, WRN, RECQL4, FANCJ, and FANCD2 in the indicated samples. Relative expression normalized to GAPDH, mean ± SD (n = 3). C p53 inactivation leads to increased FANCD2 protein levels. Protein extracts, prepared from TP53 wt and p53-inactivated Ctrl or ATRX KO NGP cells, were immunoblotted with antibodies against FANCD2 and β-Tubulin. D Real-time RT-PCR analysis of G4-resolving helicase genes and FANCD2 in Ctrl and ATRX KO SK-N-AS cells. Relative expression normalized to GAPDH, mean ± SD (n = 3). E Western blot analysis of FANCD2 in Ctrl and ATRX KO SK-N-AS cells. β-Tubulin served as a loading control.