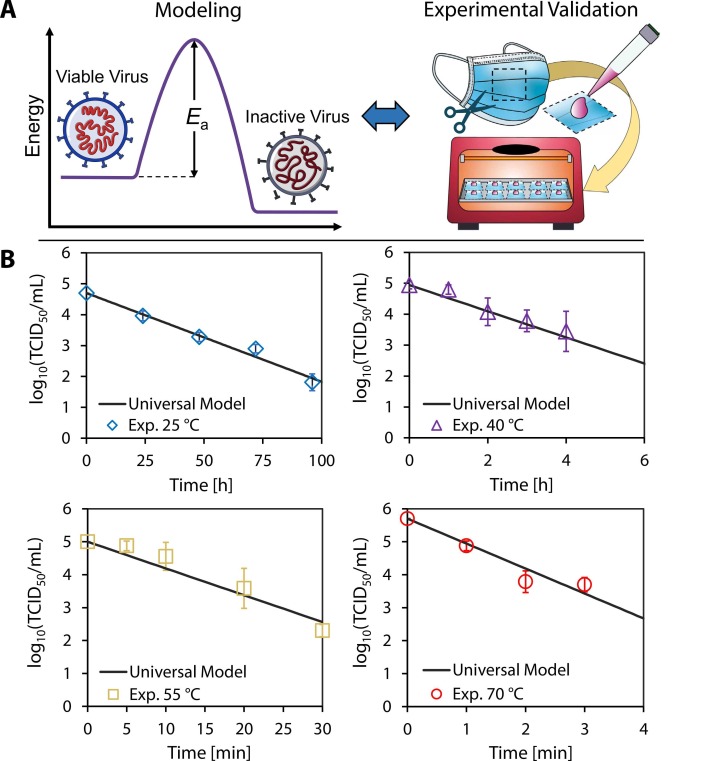
Fig. 1.
Validation of model with experimental results. (A) The universal model combines the rate law and the Arrhenius equation to determine the activation energy required to inactivate a specific virus. Surgical mask samples were inoculated with SARS-CoV-2 and exposed to 25 °C, 40 °C, 55 °C, and 70 °C dry heat in an oven. (B) The samples were assayed at different times; the plots show the corresponding log10 viable virus concentration at each time point for a given temperature. Each experimental data point was assayed in triplicate, and error bars correspond to the standard deviation among the triplicate measurements. Our universal model based on the reaction kinetics was plotted, and exhibited close agreement with experimental data.