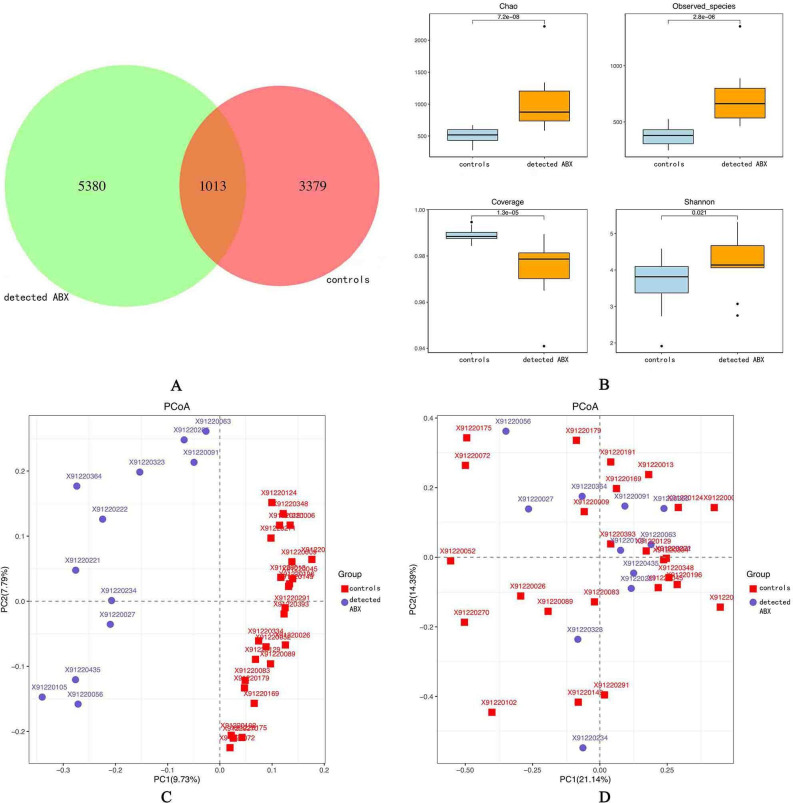
Figure 1.
Richness and diversity of the gut microbiota in pregnant women who had been exposed to antibiotics (ABX) and those who had not. (A) Venn diagram of exposure to ABX in pregnant women; controls had not been exposed to ABX while detected ABX had. Detected ABX had more operational taxonomic units than controls. (B) Alpha diversity was calculated using QIIME2 V.2018.2 based on a sequence similarity level of 100%, including the Chao richness estimator, observed species, coverage, and the Shannon diversity index. Detected ABX showed higher alpha diversity than controls. Principal coordinates analysis based on the unweighted UniFrac matrix (C) and weighted UniFrac matrix (D) showed that the overall fecal microbiota composition was different between the two groups. Each point represents one sample of antibiotic exposure (red, controls, n=25; blue, detected ABX, n=12). The distances between different samples reflect the comparability of the two groups.