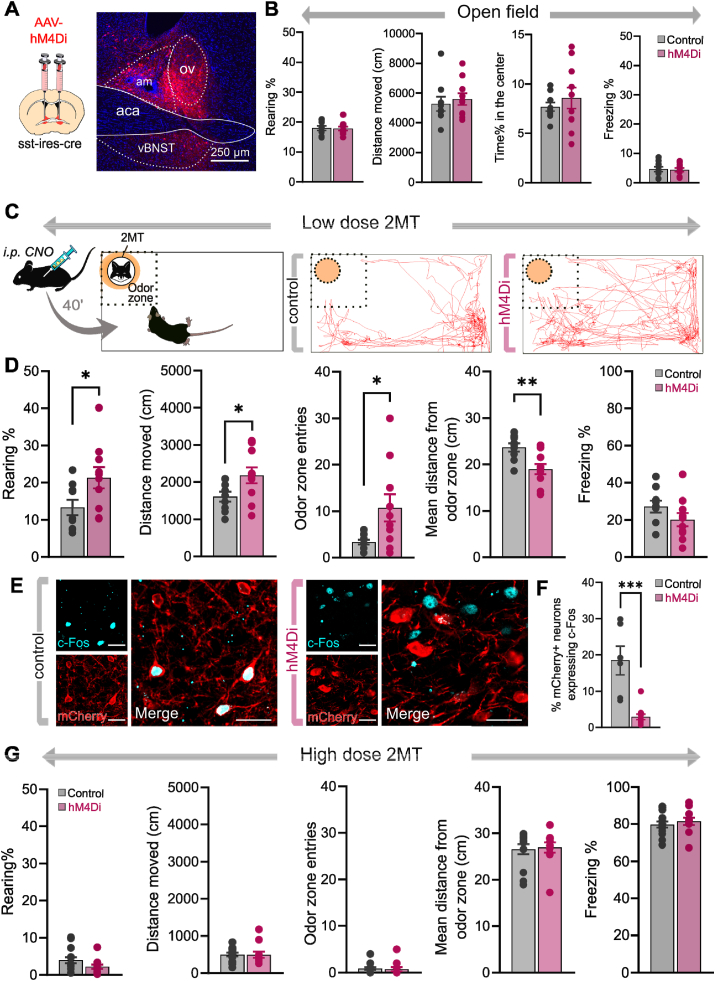
Fig. 2.
Chemogenetic inhibition of BNSTSSTneurons reduces fear response under weak threat. (A) Schematics of stereotaxic delivery of AAVs encoding hM4Di inhibitory DREADD receptors or control fluorophore in sst-ires-cre mice, and representative photomicrograph illustrating hM4Di-mCherry expression 4–6 weeks later. (B) Exploratory and anxiety-like behaviors in an open field arena were not altered by chemogenetic inhibition of BNSTSST neurons. (C) Illustration of experimental settings and representative trajectory plots of individual 2MT-exposed mice expressing control fluorophore or hM4Di receptors. (D) Innate fear responses during low-dose 2MT exposure were blunted by chemogenetic inhibition of BNSTSST neurons. (E) Representative confocal microscopic images of c-Fos expression in the BNST from 2MT-exposed mice expressing control fluorophore or hM4Di receptors (40 min after CNO injection). (F) hM4Di-expressing neurons exhibited reduced neuronal activity during 2MT-exposure compared to controls indicated by decreased cFos+/mCherry + co-labeling. Scale bars represent 25 μm. (G) Chemogenetic inhibition had no effect on fear responses in case of high dose of 2MT exposure. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (Student t-test), ***p < 0.001 (Mann-Whitney test). Abbreviations: aca: anterior commissure, am: anteromedial BNST, ov: oval nucleus of BNST, vBNST: ventral BNST.