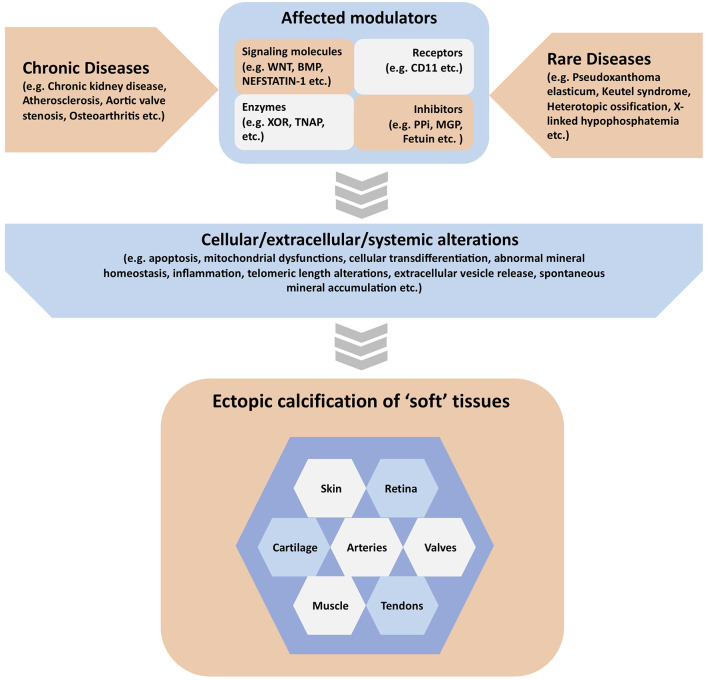
Figure 1.
Graphical summary of the contents covered in the manuscripts published in the special issue. Ectopic calcification in various “soft” tissues can be associated with both chronic and rare diseases. These diseases may affect one or more modulators of “soft” tissue calcification, which include but are not limited to signaling molecules, receptors, enzymes, and other proteins or inorganic molecules acting as mineralization inhibitors. These activating or inhibiting modulators may in turn alter a variety of cellular, extracellular and systemic parameters in the extracellular matrix causing the initiation and progression of ectopic calcification in various “soft” tissues.