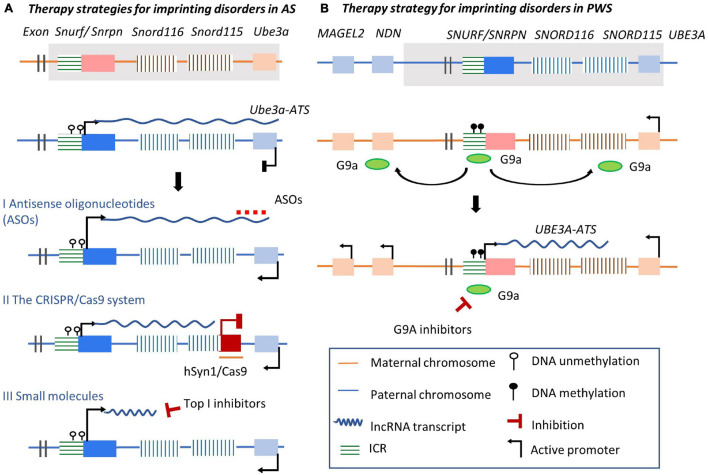
FIGURE 6.
Three state of the art strategies for imprinted disorders via targeting imprinted lncRNAs. (A) Therapeutic strategies for AS. Molecular alterations such as deletions in Ube3a/Ube3a-ATS imprinted cluster can cause the loss of effective Ube3a expression. Line I: ASOs are designed to target the overlapping regions of Ube3a-ATS transcripts and Ube3a, releasing paternal Ube3a expression; Line II: the human synapsin 1 (hSYN1) gene promoter is used drive neuron-specific expression and Cas9 packaged with adeno-associated virus delivering system is inserted into the gene region of the Snord115, leading to disrupted transcription of Ube3a-ATS before extending to the Ube3a gene encoding region. Line III: Top I inhibitors disrupt the elongation of the Ube3a-ATS at the Snord116 region. Ube3a paternal expression is released from transcriptional collision. (B) Therapeutic strategy for PWS. G9A inhibitors prevent G9A recruitment to flanking regions near the ICR, releasing Ube3a-ATS lncRNA expression from its promoter in the ICR.