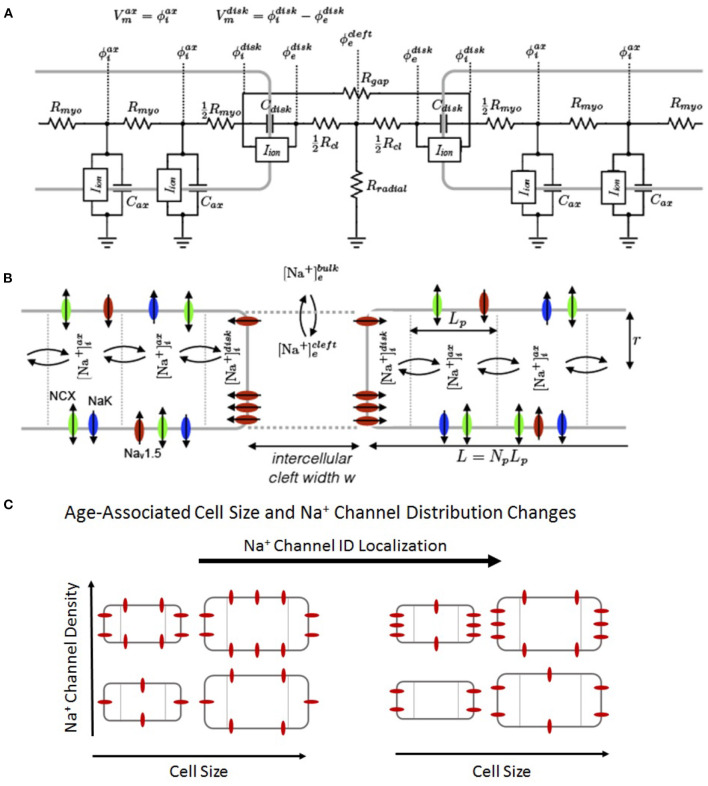
Figure 1.
Schematic of the computational model. (A) Electric circuit representation of coupled myocytes. Intracellular nodes are coupled via a myoplasmic resistance (Rmyo). End nodes are coupled via a gap junctional resistance (Rgap). Extracellular potentials at the disc and intercellular cleft ( and , respectively) are governed by a T-shaped network of two axial resistances in the intercellular cleft (Rcl) and one radial resistance (Rradial). (B) Na+concentration in diffusively coupled compartments, including intracellular Na+in the axial and disc compartments ( and ) and extracellular Na+in the intercellular cleft and bulk spaces ( and ). (C) Representation of age-associated change in model parameters, including changes in cell size (S), Na+ channel density (ρNa), and Na+channel ID localization (IDNa).