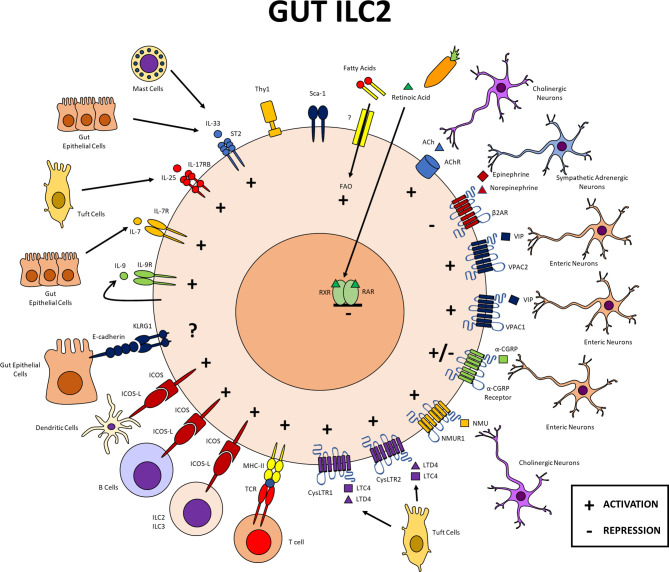
Figure 2.
Gut ILC2s. Expression of different markers in intestinal ILC2s and cellular interactions within this tissue. In the gut, ILC2s interact with other immune cells, neurons, epithelial cells, among other populations. All cytokine, leukotriene, and neuropeptide receptors mentioned in this review, except the β2AR, provide signals that activate ILC2s in the gut. CGRP both positively and negatively regulates these cells. In the gut, expression of MHCII, ICOS and its ligand favors the function of ILC2s. The function of ILC2s in this tissue depends on fatty acid oxidation, while retinoic acid inhibits ILC2s. PG, prostaglandin; LT, leukotriene; NMU, neuromedin U; CGRP, calcitonin gene related peptide; VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide; RAR, retinoid acid receptor; RXR, retinoid X receptor; fatty acids oxidation.