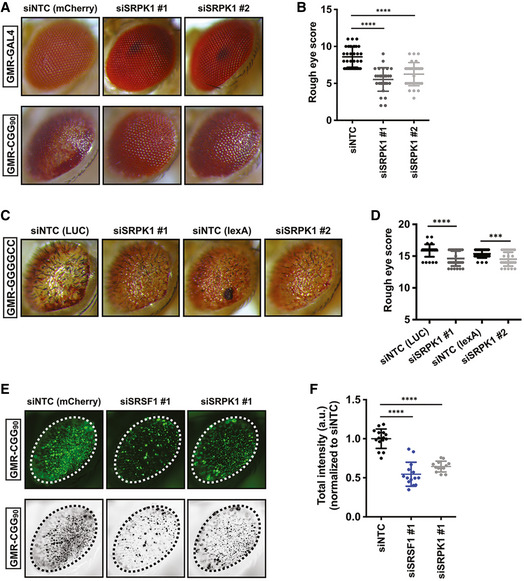
Figure 4. SRPK1 knockdown modifies CGG and GGGGCC repeat‐associated toxicity in Drosophila .
-
A, BRepresentative (A) photographs of fly eyes and (B) quantitation with siRNA‐mediated knockdown of SRPK1 (dSRPK1); n = 30–34/genotype. Error bars represent mean ± SD.
-
CRepresentative photographs of fly eyes expressing GMR‐GAL4‐driven (GGGGCC)28‐EGFP with siRNA‐mediated knockdown of SRPK1 or disruption by insertion.
-
DQuantitation of rough eye phenotypes. t‐test with Welch corrections for comparisons with the control; n = 31–34 flies/ genotype. Error bars represent mean ± SD.
-
ERepresentative external eye imaging for the detection of GFP aggregates caused by (CGG)90‐EGFP transgene expression (top). Converted images used to quantify total intensity of GFP puncta (bottom).
-
FDepletion of SRSF1 or SRPK1 by RNAi results in reduced (CGG)90‐EGFP puncta compared to control siRNA as quantified by total intensity (a.u. = arbitrary unit). n = 13–15 flies/genotype. Error bars represent mean ± SD.
Data information: Statistical analysis was performed using two‐tailed Student’s t‐test with Welch’s correction, ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.
Source data are available online for this figure.
