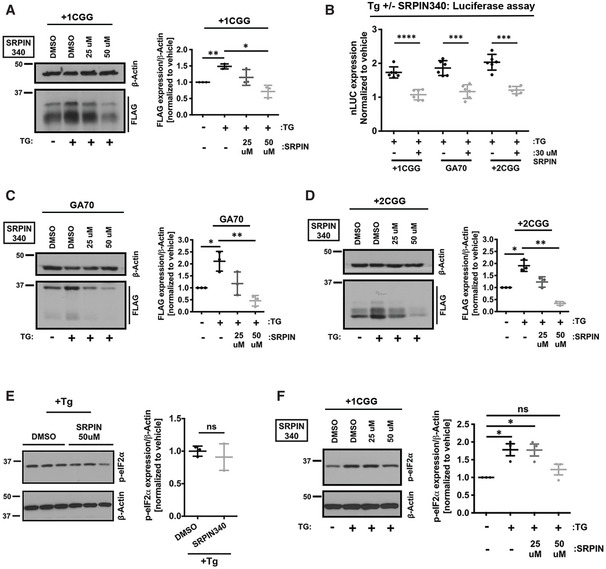
Figure 6. SRPK1 inhibition prevents stress‐induced enhancement of RAN translation.
-
AExpression of +1CGG‐nLuc‐3xFLAG RAN translation reporters in HEK293T cells treated with 2 μM TG (for stress induction) analyzed by immunoblot (n = 3 biological replicates). To evaluate effects of SRPK1 inhibition, cells were pre‐treated with DMSO or SRPIN340 before reporter transfection.
-
BRelative expression of +1CGG‐nLuc reporters in HEK293T cells (n = 6 biological replicates) following stress induction with 2 μM TG treatment. Values normalized to vehicle (DMSO) treatment. As in (A), cells were pre‐treated with DMSO or SRPIN340 before reporter transfection.
-
C, DExpression of GGGGCC‐nLuc‐3xFLAG (C) and +2CGG‐nLuc‐3xFLAG (D) RAN translation reporters in HEK293T cells treated with 2 μM TG (for stress induction) analyzed by immunoblot (n = 3 biological replicates). To evaluate effects of SRPK1 inhibition, cells were pre‐treated with DMSO or SRPIN340 before reporter transfection.
-
ESRPK1 inhibition by SRPIN340 did not alter eIF2α phosphorylation in response to 2 μM TG (for stress induction) in HEK293T cells by immunoblot (n = 3 biological replicates).
-
FSPRK1 inhibition suppressed eIF2α phosphorylation in HEK293T cells treated with 2 μM TG (for stress induction) in the presence of the +1CGG reporter. Cells were pre‐treated with DMSO or SRPIN340 before reporter transfection (n = 3 biological replicates).
Data information: Error bars represent mean ± SD. Two‐tailed Student’s t‐test with Welch’s correction. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; and ****P < 0.0001.
Source data are available online for this figure.
