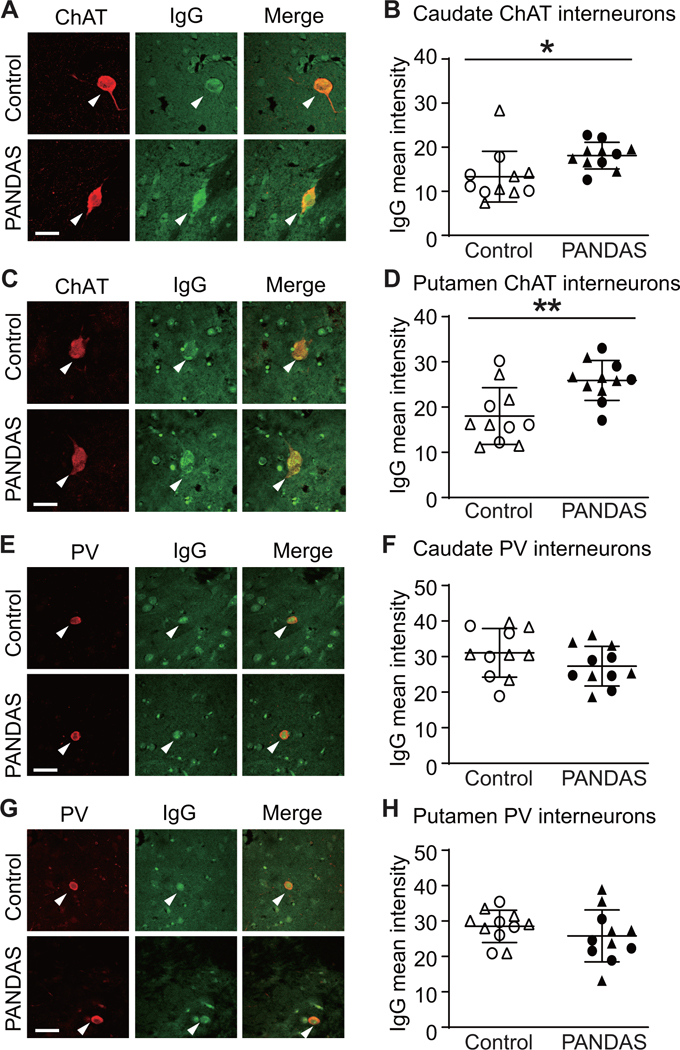
Figure 2. PANDAS IgG shows elevated binding to cholinergic interneurons in human brain slices.
(A and C) Representative confocal images of immunohistochemical staining of human IgG (green) and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT, red) in human caudate (A) and putamen (C). Arrowheads indicate human IgG binding to CINs. Scale bar: 40 μm. (B and D) PANDAS antibodies show more binding to CINs in human caudate (B) and putamen (D), relative to matched controls, as quantified by average fluorescence intensity: (B) in caudate (t[20]=2.440, p=0.024); (D) in putamen (t[20]=3.401, p=0.003). (E and G) Representative confocal images of immunohistochemical staining of human IgG (green) and parvalbumin (PV, red) in human caudate (E) and putamen (G). Arrowheads indicate human IgG binding to PV-positive interneurons. Scale bar: 40 μm. (F and H) PANDAS antibodies do not show elevated binding to PV-positive interneurons: (F) in caudate (t[20]=1.409, p=0.174); (H) in putamen (t[20]=1.042, p>0.3). All comparisons are by independent samples t-test; *p<0.05, **p<0.01; N=11 each group. ●,◯ – 10 serum from the first cohort (47); ▲,△ – 12 sera from the second cohort.