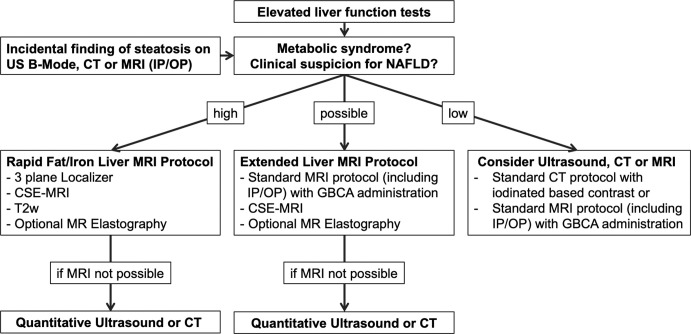
Figure 8:
Flow chart shows diagnostic imaging work-up for hepatic steatosis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In patients with abnormal liver function tests or incidental findings of hepatic steatosis at imaging and high clinical suspicion for NAFLD, a rapid MRI protocol targeted for liver fat quantification is the method of choice to estimate steatosis severity. MRI elastography might be added to assess stiffnesses of liver tissue and fibrosis presence. If the probability of having NAFLD is lower, but steatosis cannot be excluded, an extended liver protocol should be considered. CSE-MRI = chemical shift–encoded MRI, GBCA = gadolinium-based contrast agent, IP/OP = in-phase and opposed-phase imaging, T2w = T2-weighted imaging.