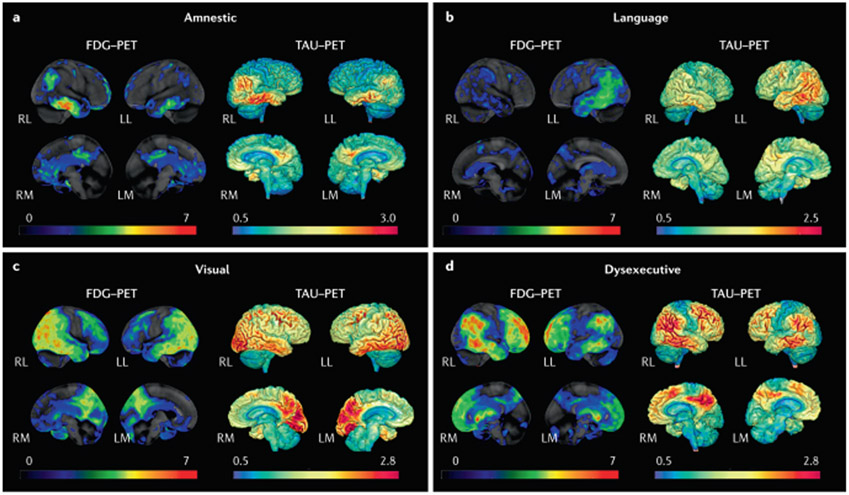
Fig. 8 ∣. Tau-PET and FDG-PET patterns in different clinical syndromes in persons with high β-amyloid-PET.
a ∣ Typical amnestic-predominant Alzheimer disease with temporoparietal hypometabolism and tauopathy. b ∣ Language syndrome (also known as logopenic variant primary progressive aphasia) with a highly asymmetric pattern in which hypometabolism and tauopathy are highly left hemisphere predominant. c ∣ Visual syndrome (also known as posterior cortical atrophy) with a pattern of hypometabolism and tauopathy that is posterior temporal, parietal and occipital lobar in distribution. d ∣ Dysexecutive syndrome with temporal, parietal and prominent frontal hypometabolism and tauopathy. Red colour on FDG-PET indicates greater hypometabolism, whereas red colour on tau-PET indicates a higher intensity of tracer retention. LL, left lateral; LM, left medial; RL, right lateral; RM, right medial.