Figure 1.
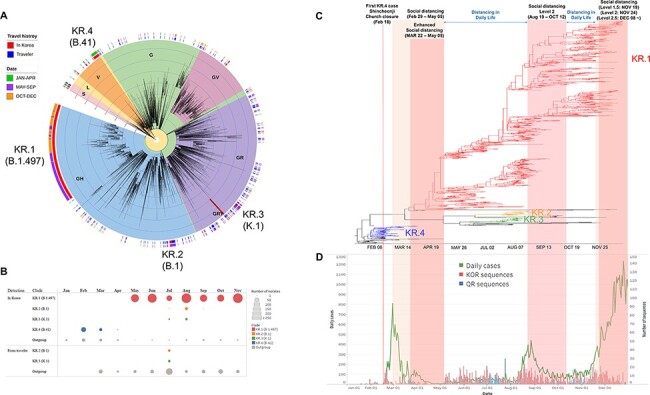
Multiple introductions of SARS-CoV-2 into South Korea. (A) Approximately maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of the 5,145 SARS-CoV-2 full genomes. The SARS-CoV-2 viruses detected from travelers entering South Korea or their direct contacts were annotated by blue color strips, and viruses detected from South Korean residents with no travel history were annotated by red color strips. Internal tree scales for branch lengths indicate nucleotide substitutions per site. (B) The number of sequences of each Korean subgroup in each month. The viruses that do not belong to KR.1–4 were classified as outgroup. (C) A time-scaled maximum clade credibility tree of all SARS-CoV-2 detected from South Korean residents. Branches are colored according to the Korean subgroups detected in Fig. 1A. (D) The daily case number of SARS-CoV-2 (left axis) and the number of analyzed sequences (right axis) in South Korea.
