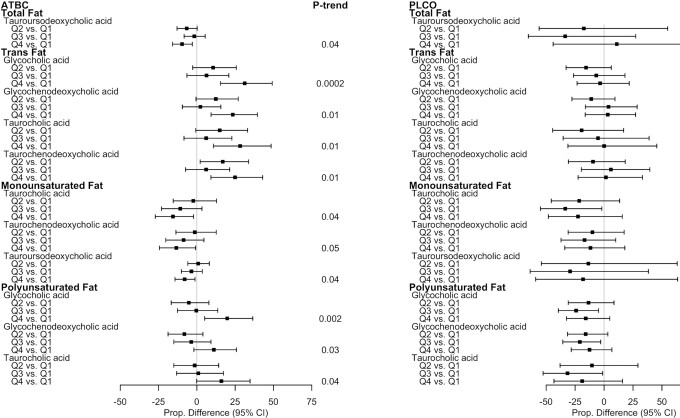
FIGURE 5.
Proportional differences in circulating BAs by quartiles of fat and fat subtype intake in ATBC (n = 2224) and PLCO (n = 986). All statistically significant findings (FDR P value < 0.05) are presented with the corresponding BAs in the other study population to facilitate interpretation. ATBC study linear regression models were adjusted for case status (colorectal cancer, liver disease, biliary cancer, liver cancer, or control), age at randomization, total cigarettes smoked/d, total duration of smoking (y), physical activity level (≥3 times/wk, 1–2 times/wk, or <1 time/wk), BMI (kg/m2), level of education (less than elementary to part of junior high school or greater than junior high school), total energy intake (kcal/d), coffee intake (drinks/d), alcohol intake (drinks/d), and fiber intake (energy residual-adjusted g/d). PLCO linear regression models were adjusted for colorectal cancer case status, age at diet questionnaire completion, sex, total cigarettes smoked/d, total duration of smoking (y), physical activity level (≥ 3 h/wk, 1–2 h/wk, or <1 h/wk), BMI (kg/m2), level of education (high school education or less, some college or postcollege training, college graduate and more), total energy intake (kcal/d), coffee intake (drinks/d), alcohol intake (drinks/d), and fiber intake (energy residual-adjusted g/d). The P-trends were corrected using FDR correction with the Benjamini-Hochberg method. Dietary component quartiles were based on energy-adjusted dietary estimates, using a residual method. Abbreviations: ATBC, Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta-Carotene Cancer Prevention Study; BA, bile acid; FDR, false discovery rate; PLCO, Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial; Q, quartile.