Figure 1 .
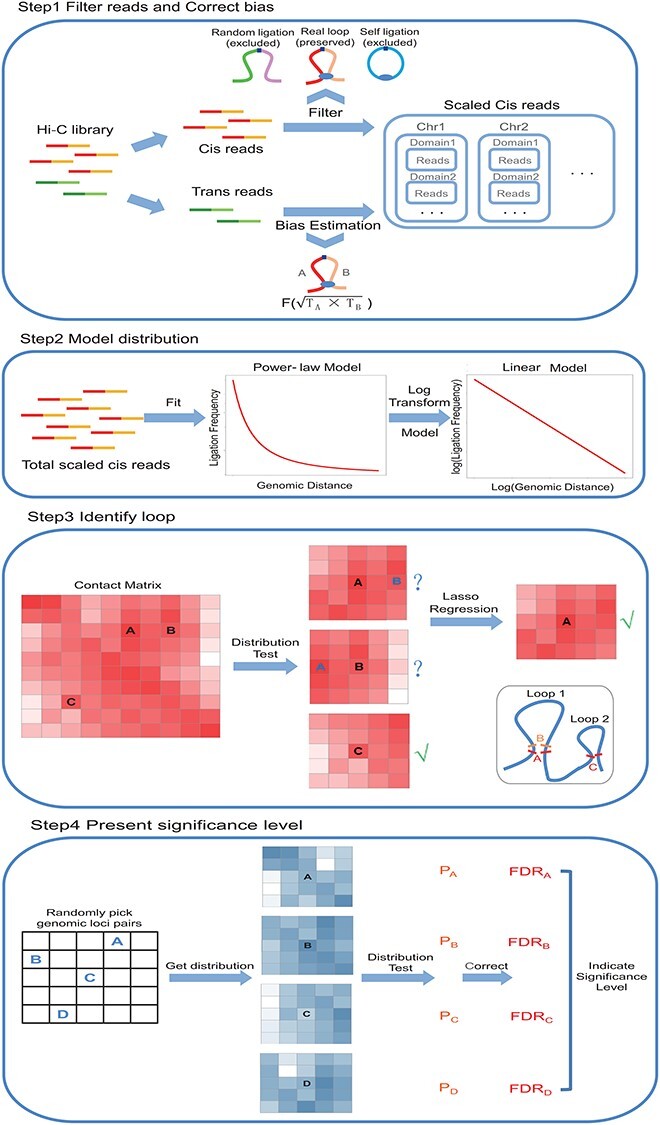
Schematic overview of Chrom-Lasso. The overall analysis strategy of Chrom-Lasso involves four steps. Step1 is to filter the random-ligation reads and self-ligation reads from the Hi-C library and to take the trans (inter-chromosomal) reads as the reflection of biases resulting from the Hi-C experiment and high throughput sequencing to estimate biases for further detecting functional interactions. Step2 focuses on modeling the distribution between ligation frequency and genomic distance which fits linear distribution after log transformation. Step3 detects true chromatin interactions based on testing whether the potential interacting center and its surrounding reads fit the distribution modeled in Step2, and when two or more potential interaction centers are detected within a user-defined neighborhood region (e.g. interaction center A and B), it performs lasso regression to determine the iinteracting center(s) fit the model the best. Step4 is to calculate the FDR for interactions according to a background P-value distribution inferred by randomly picking genomic loci pairs and testing their reads distribution.
