Figure 4 .
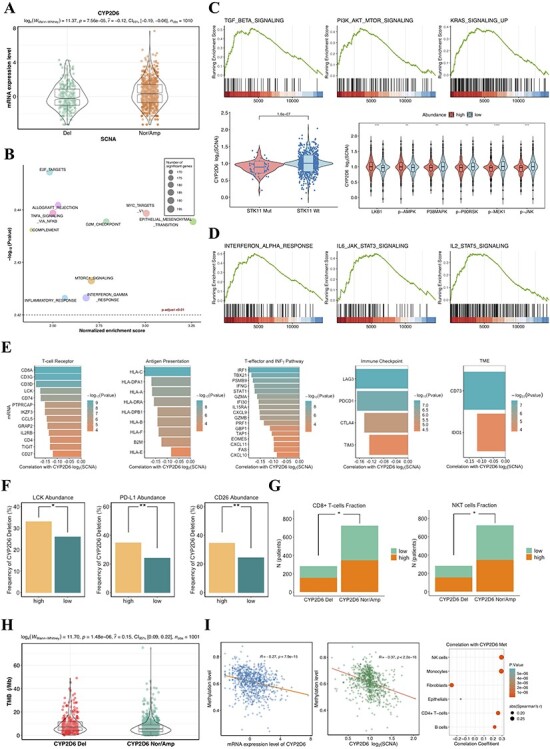
(A) The SCNA of CYP2D6 significantly associated with mRNA expression. (B) The top 10 of prominently enriched pathways for CYP2D6 loss (sorted by normalized enrichment score). (C) Top, three representative GSEA plots for carcinogenesis pathways that were significantly enriched (adjusted P < 0.01). Bottom left, copy number of CYP2D6 related to mutational status of STK11; Bottom right, proteomic analysis showing correlation between CYP2D6 SCNA and the abundance of relevant proteins involving MTOR and MAPK pathways. (D) Three representative GSEA plots for immunomodulatory pathways that correlated with CYP2D6 loss (adjusted P < 0.01). (E) Associations of CYP2D6 SCNA with mRNA expression of 48 immune-related genes. CYP2D6 deletion correlated to PD-L1, LCK, CD26 protein expressions (F), lymphocyte abundance (G) and TMB (H). (I) Relationships between methylation levels and mRNA expressions (left) as well as copy number of CYP2D6 (middle). Tumors with hypermethylated CYP2D6 presenting higher fractions of immune cells (right). Del: deletion; Nor/Amp: normal/amplification; SCNA: somatic copy number alteration; Met: methylation.
