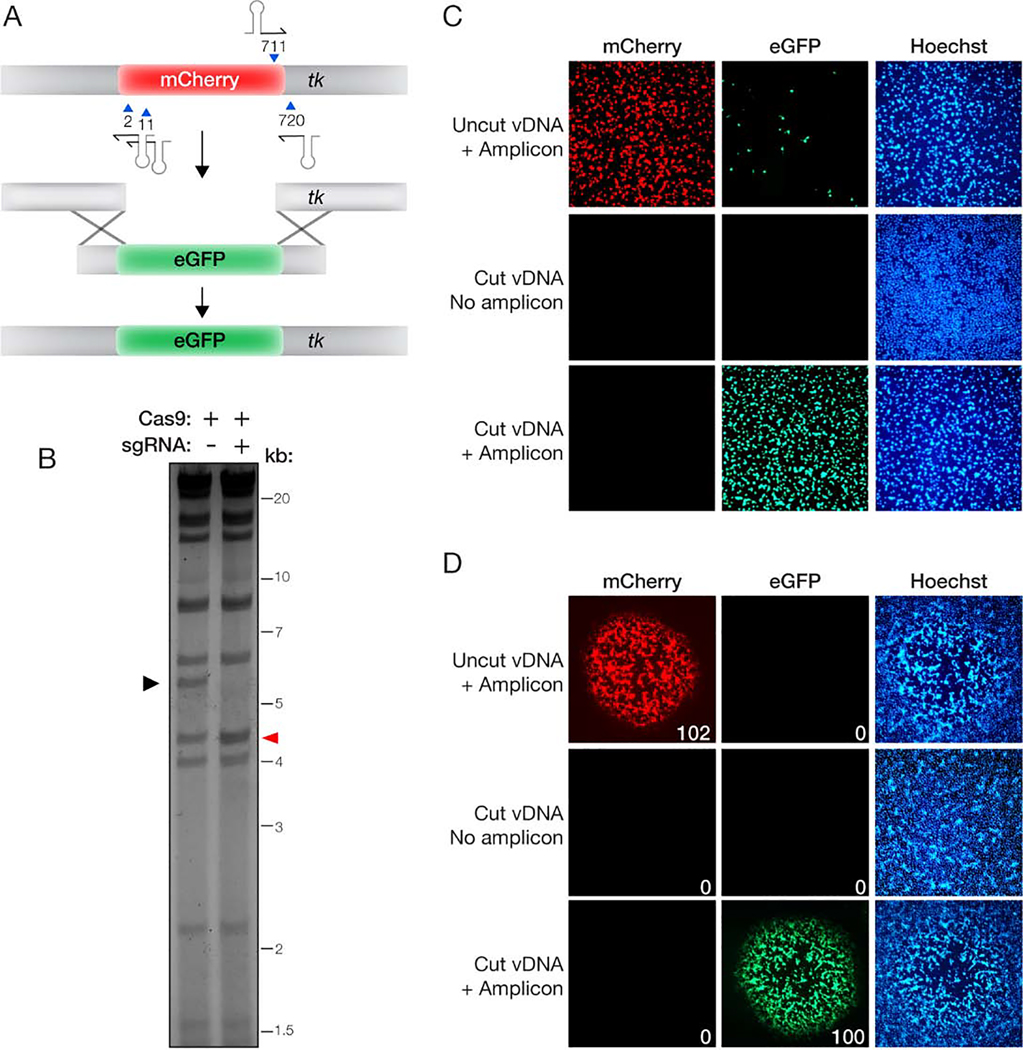
Figure 1. Efficient exchange of fluorescent reporters with MAVERICC.
(A) Overview of the strategy to exchange an eGFP reporter for an mCherry reporter currently in the tk locus. The parental vDNA was cut with Cas9 directed by four sgRNAs (stem-loop and blue arrowhead) as shown. Homologous recombination (‘X’ shapes) between the transfer amplicon and cleaved vDNA promotes genome repair and insertion of eGFP. The numbers denote the first nucleotide of the PAM sequence for each sgRNA, with numbering beginning at the ‘A’ in the mCherry start codon. (B) vDNA (incubated with Cas9 without or with sgRNAs) was fragmented by HindIII digestion, resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis, and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. Black arrowhead, DNA fragment containing the mCherry reporter gene. Red arrowhead, vDNA fragment that is produced by Cas9 cleavage (4,505 bp) comigrating with the HindIII K fragment (4,530 bp). (C) Fresh cells were exposed to viral rescue samples and examined for mCherry or eGFP reporter expression by fluorescence microscopy at 24 h post-infection. (D) Viral rescue samples were subjected to plaque assay and individual viral plaques were randomly selected and enumerated as mCherry-positive or eGFP-positive (total red or green plaques shown in the lower right corner of individual plaque images). No plaques were observed in rescue samples that received cleaved vDNA but no transfer amplicon (middle row).