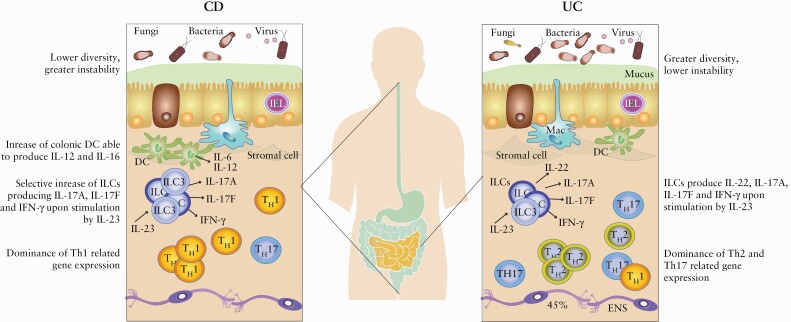
Figure 1.
Comparison of factors that differ between UC and CD. There are remarkable differences between patients with diagnoses UC and CD, but also great heterogeneity within these patient groups. Generally, CD patients have, for example, lower diversity and greater instability in their microbiota compared with UC patients.50,58,61 Also, in both CD and UC, ILCs produce IL-22, IL-17A, IL-17F, and IFN-γ upon stimulation by IL-23, but in CD there is a selective increase in IL-17A, IL-17F, and IFN-γ producing ILCs.92 Further, in CD, colonic DC show increased expression of IL-12 and IL-16 during inflammation compared with UC patients.86 Also, CD is characterised by intestinal dominance of Th1-related gene expression, whereas Th2- and Th17-related gene expression dominates in UC.108 CD, Crohn’s disease; UC, ulcerative colitis; IL, interleukin; Th, T helper cell; ILC, innate lymphoid cell; IEL, intestinal epithelial lymphocyte; Mac, macrophage; ENS, enteric nerve system; DC, dendritic cell; RA, retinoic acid; TNF, tumour necrosis factor.