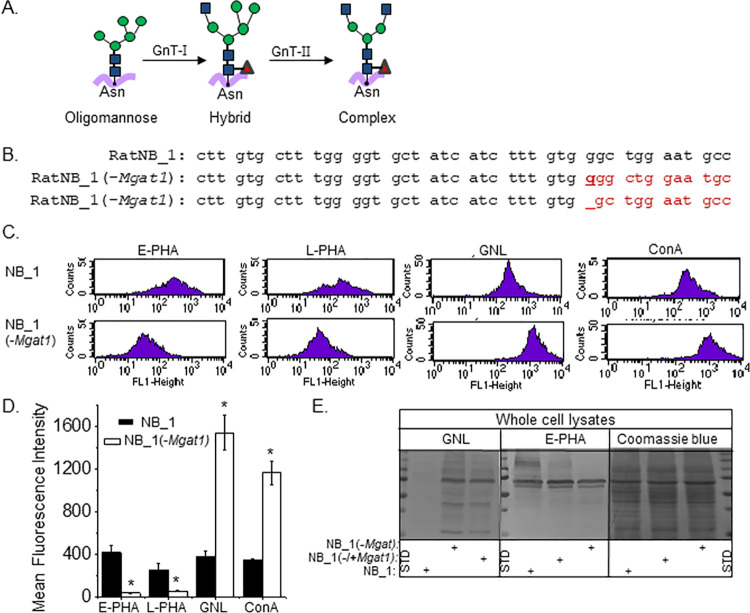
Fig 1. Characterization of a neuroblastoma cell line with knockout of GnT-I.
(A) The simplest N-glycan is oligomannose which gives rise to more mature N-glycans, hybrid and complex. GnT-I converts oligomannose to hybrid, and subsequently GnT-II converts hybrid to complex. (B) The coding sequence of rat Mgat1 from 25 to 66 was compared to that isolated from a newly created NB_1(-Mgat1) cell line. Two frameshift mutations were identified, including an inserted g nucleotide and a deletion of a g nucleotide as indicated in bold red font and dash line, respectively. Further the next in-frame start codon does not occur until residue 251 (C) Typical flow cytometry plots of NB_1 (top panels), and NB_1(-Mgat1) (bottom panels) cell lines interacting with fluorescently labelled lectins. (D) Mean fluorescence intensity of E-PHA (n = 5), L-PHA (n = 5), GNL (n = 5) and ConA (n≥2) bound to NB_1 and NB_1 (-Mgat1) cells. Graph denotes mean ± SEM and were compared by student’s t-test (*p < 0.01). (E) Lectin blots and a coomassie blue stained gel of proteins from whole cell lysates of NB_1 and NB_1(-Mgat1) cell lines. Vertical dotted and solid lines denote gel lane dividers and a different gel, respectively. Molecular weight standards (STD) in kDa: 250; 150; 100; 75; 50; and 37 from top to bottom.