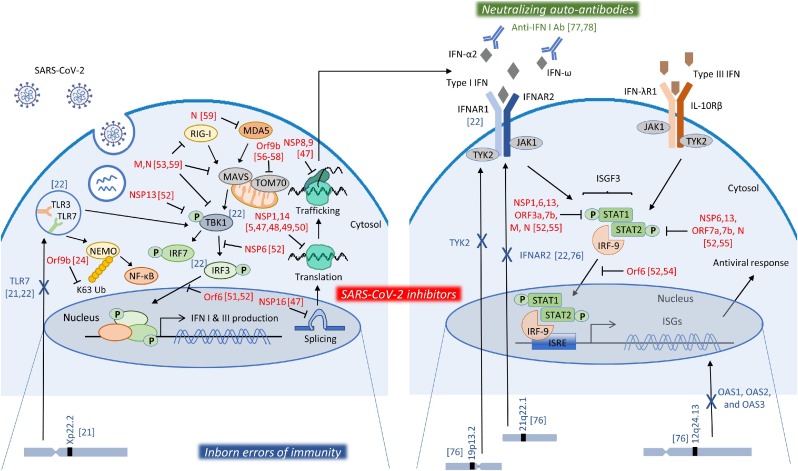
Fig. 1.
Mechanisms of impairment of the IFN response. SARS-CoV-2, after entering the cells, is recognized by PRRs, like TLR3, TLR7, RIG-I and MDA5, to initiate signaling pathways that induce that production of type I and III IFNs. IFNs bind to their receptors in the same or nearby cells to activate pathways that lead to the induction of ISGs and the initiation of the antiviral response. SARS-CoV-2 viral products have been shown to inhibit various steps of these processes, depicted in red, suppressing thus the IFN response. Moreover, genetic mutations in key molecules of these pathways, depicted in blue, have been linked to impaired immune responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Finally, auto-antibodies against type I IFN family members, depicted in green, constitute another mechanism of impaired IFN response detected in severe cases of COVID-19. Numbers in brackets [#] correspond to literature references of this review.