FIGURE 2.
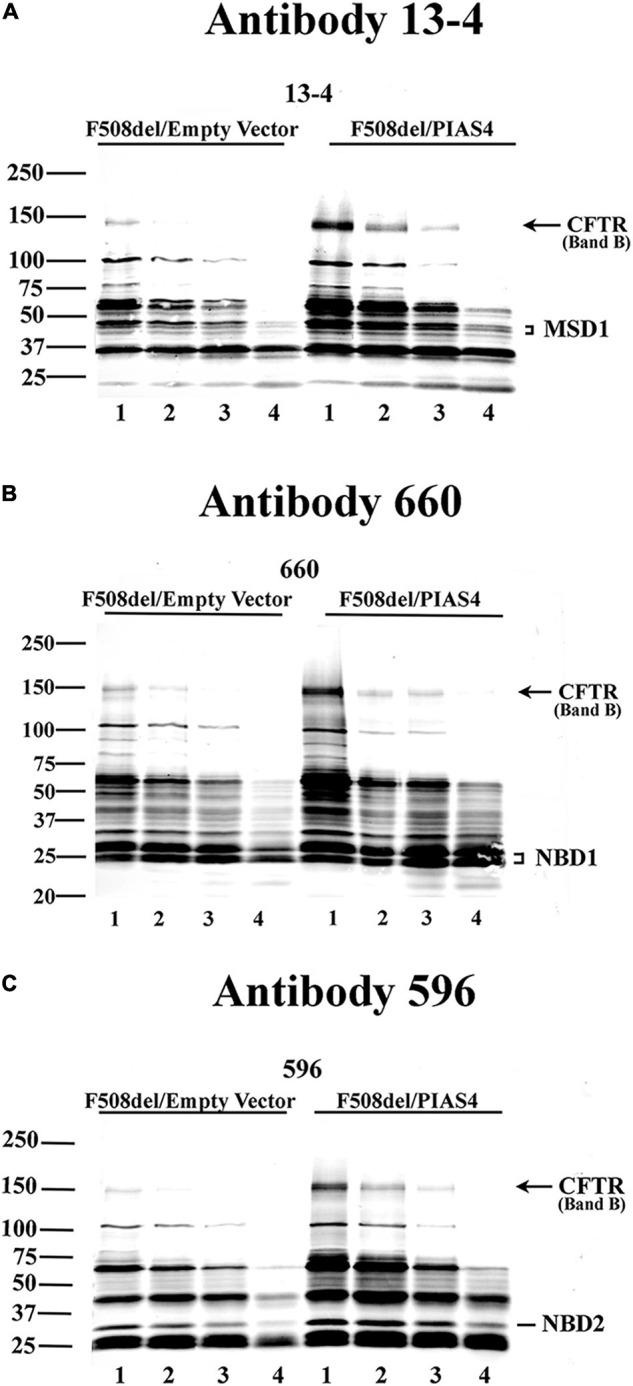
The impact of PIAS4 on the protease sensitivity of F508del CFTR. Microsomal vesicles were isolated from transfected CFBE-F508del cells and subjected to cellular disruption as described in the “Materials and Methods” section. The microsomal pellet was subjected to 20, 40, 80, or 240 μg/ml TPCK trypsin, lanes 1–4, respectively, for 15 min each, resolved on 7%/12% step gels and transferred. (A) Proteins were blotted with CFTR monoclonal 13-4 targeting the CFTR N-terminus. PIAS4 augmented band B expression and protected CFTR tryptic fragments generated by trypsin-mediated hydrolysis. Quantitation of the 13-4 gel yielded relative density values: at MW bands of 50–75 kDa, for control: 1.0, 0.54, 0.34, and 0.056; and for PIAS4 treated: 1.0, 0.80, 0.40, and 0.11. Density at MW bands ∼40–50 kDa for control: 1.0, 0.56, 0.40, and 0.16; and for PIAS4 treated: 1.0, 0.75, 0.46, and 0.29. (B,C) Other anti-CFTR monoclonals gave qualitatively similar results that identified fragment patterns for NBD1 (Ab #660) or NBD2 (Ab #596), respectively, which also provided evidence of protease protection. Thus, the densities of identifiable domains of F508del CFTR were increased for all fragments, as PIAS4 stabilized domain fragments against protease activity.
