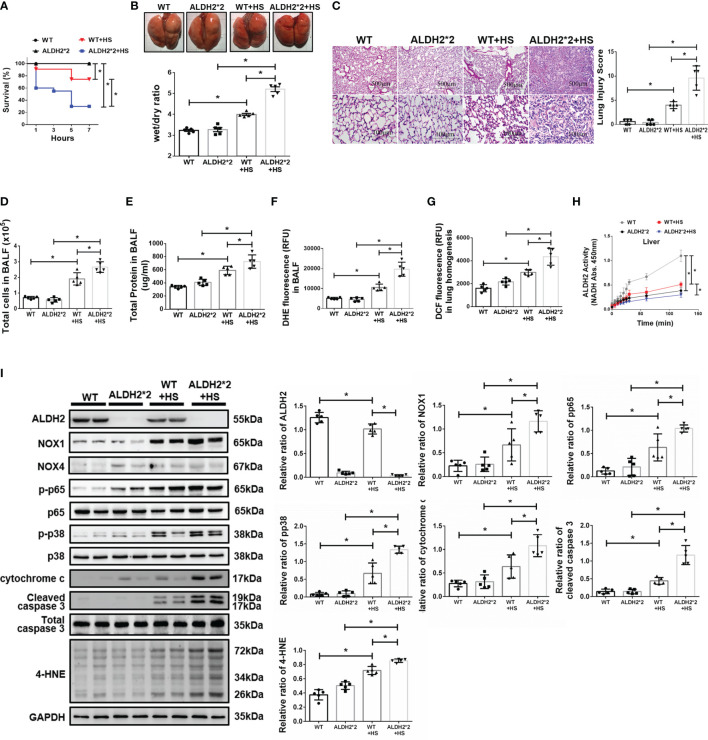
Figure 1.
Effects of ALDH2 on HS-induced ALI in vivo. C57BL/6J WT and ALDH2*2 KI mice were exposed to WBH (42°C, 80% RH for 1 h) and then analyzed. (A) Survival of mice subjected to WBH (n = 20 in each group). (B) Representative images of the lungs and wet/dry ratio of the lungs (n = 5). (C) H&E stain of the lungs (n = 5). (D) Total cells in the BALF (n = 5). (E) Total protein in the BALF (n = 5). (F) ROS production in the BALF as determined by DHE fluorescence measurement using a fluorescence microplate reader with an excitation wavelength of 518 nm and an emission wavelength of 606 nm (n = 5). (G) ROS production in lung homogenates as determined by DCF fluorescence measurement using a fluorescence microplate reader with an excitation wavelength of 488 nm and an emission wavelength of 535 nm (n = 5). (H) The ALDH2 activity in liver homogenates was measured by NADH production using the O.D. absorbance at 450 nm in a microplate reader (n = 5). (I) The protein and 4-HNE levels in lung homogenates were measured by immunoblotting. Densitometric analysis was conducted with imaging processing software. The data were quantified by normalization to GAPDH; phosphorylated proteins were normalized to total proteins (n = 5). The data are expressed as the mean ± SD. Statistical significance is indicated as *p < 0.05.