FIGURE 3.
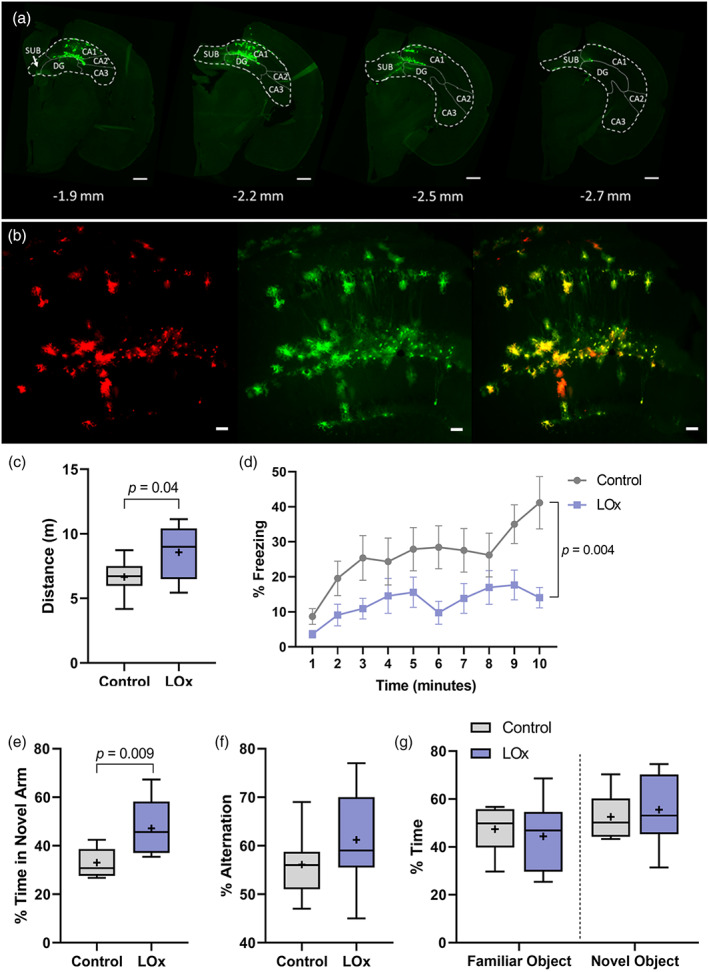
Expression of lactate oxidase (LOx) in hippocampal astrocytes leads to novelty‐induced activity. (a) Serial coronal sections of the mouse brain with control vector (LVV‐sGFAP‐IRES‐tdTomato) injection in the hippocampus and stained with anti‐RFP (green); scale bars 500 μm. (b) Representative images of hippocampal sections with tdTomato+ astrocytes (red) co‐stained with anti‐RFP (green); scale bars – 50 μm. (c) In the holeboard test mice expressing LOx in hippocampal astrocytes manifested increased activity compared to control LVV injected mice; (d) During habituation to the trace fear conditioning chamber, mice expressing LOx in hippocampal astrocytes showed less freezing in response to a novel environment; *p < 0.05, n = 8–9. (e) Hippocampal LVV‐sGFAP‐LOx‐IRES‐tdTomato injections improved the performance in the task for spatial recognition memory in the Y maze task, with no change in the y‐maze spontaneous alternation task (f) or the novel object recognition test (g); **p < 0.01, n = 5–9 [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
