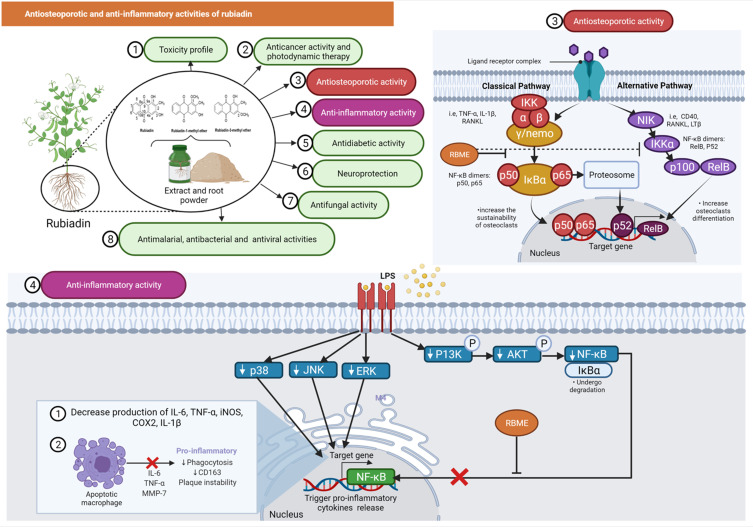
Figure 7.
Antiosteoporotic and anti-inflammatory activities of rubiadin. Inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) phosphorylation and degradation of nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor alpha (IκBα) by RBME suggests that it could be used to treat bone disorders characterized by excessive bone resorption. RBME demonstrated anti-inflammatory activity by decreasing pro-inflammatory markers while increasing the apoptotic rate of macrophages.
Note: Created with BioRender.com.
Abbreviations: TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-1ß and 6, interleukin 1 beta and 6; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand; IKKγ/NEMO, nuclear factor-kappa B essential modulator; IkBα, nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha; IKKα, inhibitory kappa B kinase α; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NIK, NF-κB inducing kinase; CD40 & 163, cluster of differentiation 40 and 163; LTß, lymphotoxin beta; RelB, RELB proto-oncogene, NF-KB subunit; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; P13K, phosphoinositide 3-kinases; AKT, protein kinase B/AKT; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; COX2, cyclooxygenase-2; MMP-7, matrix metalloproteinase-7.