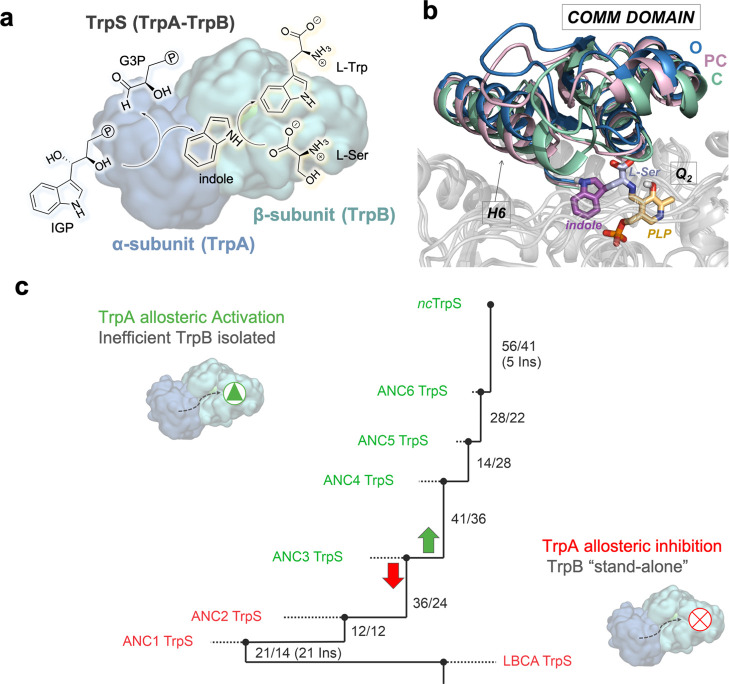
Figure 1.
Overview of TrpS enzyme. (a) Functional unit of TrpS consists of a heterodimer, which is formed by TrpA (blue) and TrpB (green). TrpA catalyzes the cleavage of IGP to G3P and indole, which in TrpB reacts with activated l-Ser in a multistep mechanism to yield l-Trp (see Scheme S1). (b) Overlay of pfTrpS metastable conformations from previous computational exploration showing the transition of the COMM domain (residues 97–184) from an open (blue, O), to a partially closed (pink, PC) to a closed conformation (green, C). Highlighted are the α-helix H6 of the COMM domain (residues 174–164) and the reaction intermediate Q2 in the active site. The parts of the Q2 intermediate are colored depending on the respective precursor molecule (PLP cofactor in orange, l-Ser in blue, and indole in purple).32 (c) Phylogenetic tree shows the path from the LBCA TrpS over six intermediate nodes (ANC1 TrpS to ANC6 TrpS) to the extant Neptuniibacter caesariensis TrpS.43 Numbers next to each edge indicate the number of mutations accumulated in TrpA and TrpB with respect to the previous node. While LBCA TrpB gets deactivated by TrpA and exhibits stand-alone function, the allosteric effect of TrpA is reverted along the phylogenetic tree with a switch between ANC2 TrpS and ANC3 TrpS to an allosteric activation, as observed in extant ncTrpS.