Figure 1.
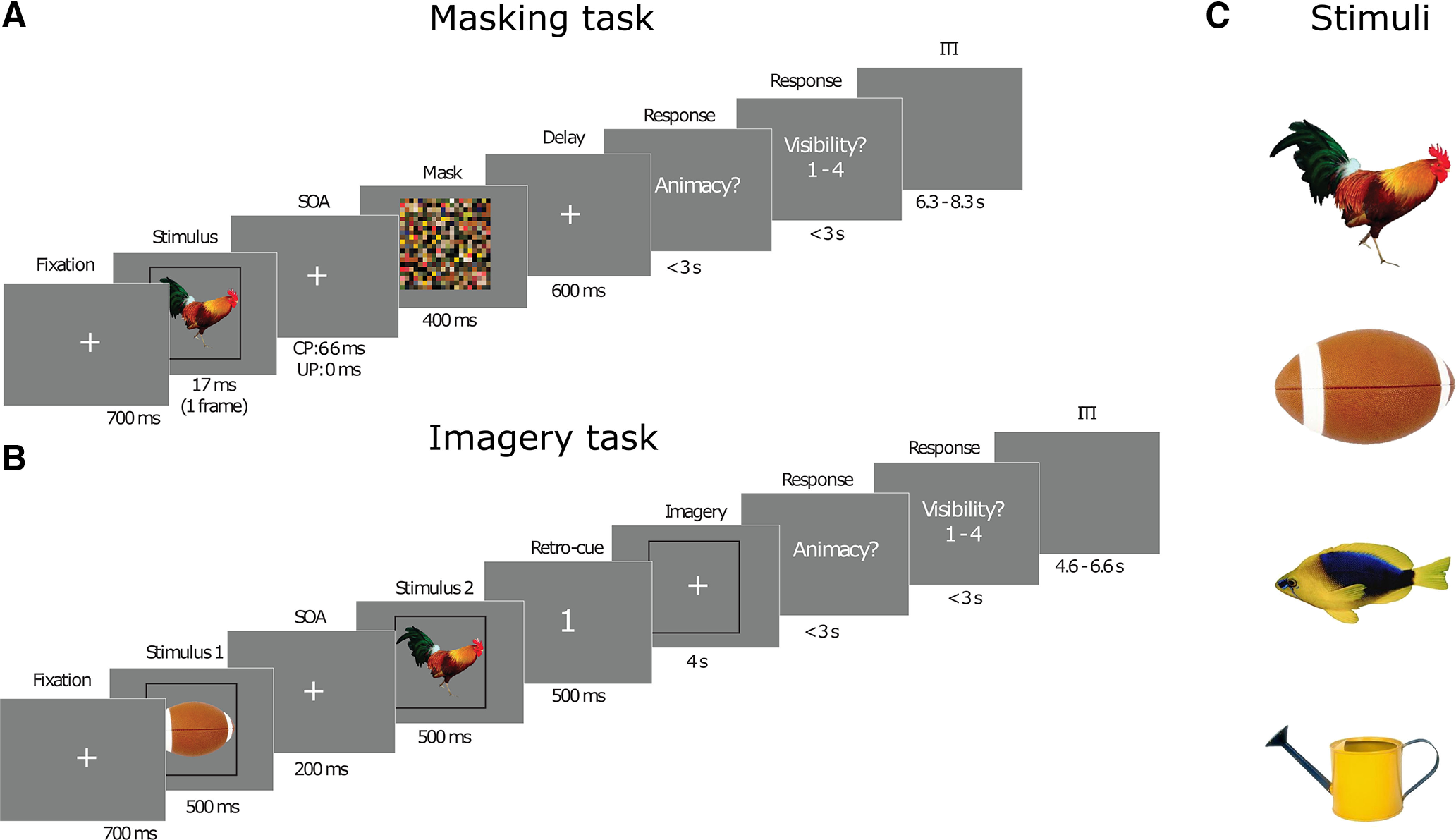
Experimental paradigm. A, Masking task. A stimulus is presented for 17 ms, followed by a mask (duration, 400 ms) after 0 ms (unconscious condition) or 66 ms (conscious condition). Participants had to indicate whether the stimulus was animate or inanimate and rate the visibility. B, Visual imagery task. Participants were presented with two stimuli after each other followed by a cue indicating whether to imagine the first or the second stimulus, as vividly as possible. After the imagery, participants had to indicate whether the imagined stimulus was animate or inanimate and rate the visibility of their imagery. C, Stimuli used: a rooster, a football, a fish, and a watering can from the POPORO stimulus dataset (Kovalenko et al., 2012). The neural analyses focused on pairwise comparisons between all possible combinations of stimuli.
