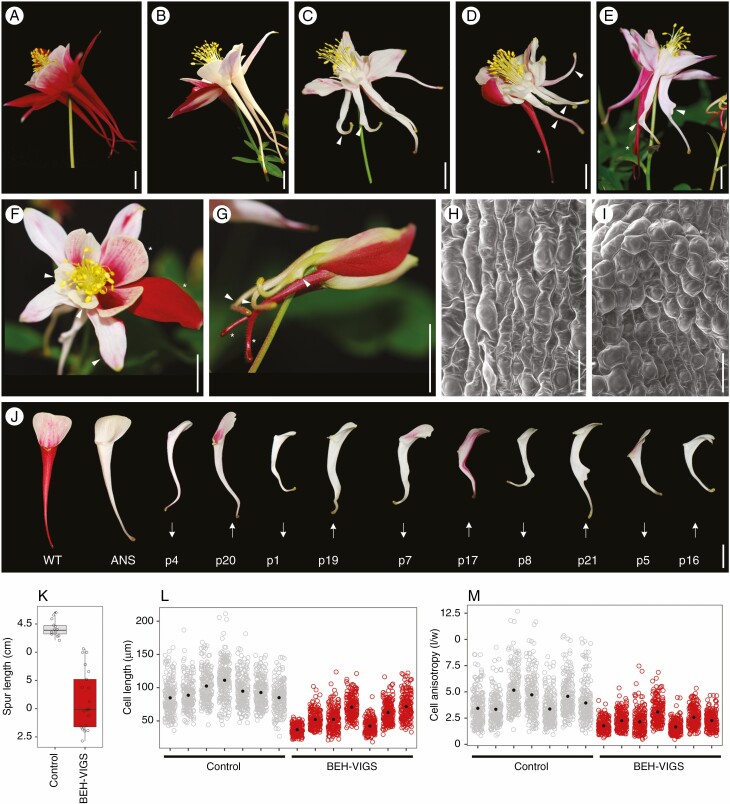
Fig. 3.
Phenotypes of BEH-VIGS; petal spurs are short, twisted or bent. (A) A mature, wildtype A. coerulea flower. (B) A mature, ANS control flower, with three phenotypically normal white petals. (c) Mature BEH-VIGS flower with petals with bends in the lower part of spur and a spur with a 90° bend and abaxial outgrowth (arrowheads). (D) Mature BEH-VIGS flower with three short petal spurs (arrowhead), and one phenotypically normal petal spur (asterisk). (E) Mature BEH-VIGS flower with petal spurs with a twisted petal and abaxial outgrowths (arrowheads), compared with two phenotypically normal spurs (asterisk). (F) Mature BEH-VIGS flower showing phenotypically normal sepals and petal blades (asterisks), compared with small sepals and petal blades (arrowheads). (G) Young BEH-VIGS flower with petal spurs with abaxial outgrowths and 90° bends in the lower spur (arrowheads), compared with two phenotypically normal petal spurs (asterisks). (H) SEM of ANS control lower spur showing anisotropically elongated cell and parallel files of cells in the lower spur. (I) SEM of BEH-VIGS lower spurs showing short, misaligned cells. (J) Comparison of WT, ANS control and BEH-VIGS petals (p). Arrows indicate if a BEH-VIGS petal showed decreased (down) or increased (up) relative expression of AqBEH genes (see Fig. 4). (K) Measurements of petal spur lengths in control (n = 14, mean 4·42 cm) and BEH-VIGS (n = 21, mean 3·14 cm) petals. Welch t-test, P < 0·0001. (L) Cell lengths of ANS control (mean 94·2 μm) and BEH-VIGS petal spurs (mean 55·5 μm). Welch t-test, P < 0·0001. (M) Cell anisotropy of ANS control (mean 4·1) and BEH-VIGS petals spurs (mean 2·3). Welch t-test, P < 0·0001. Scale bars: (A–G, J) = 1 cm; (H–I) = 50 μm.