Figure 3.
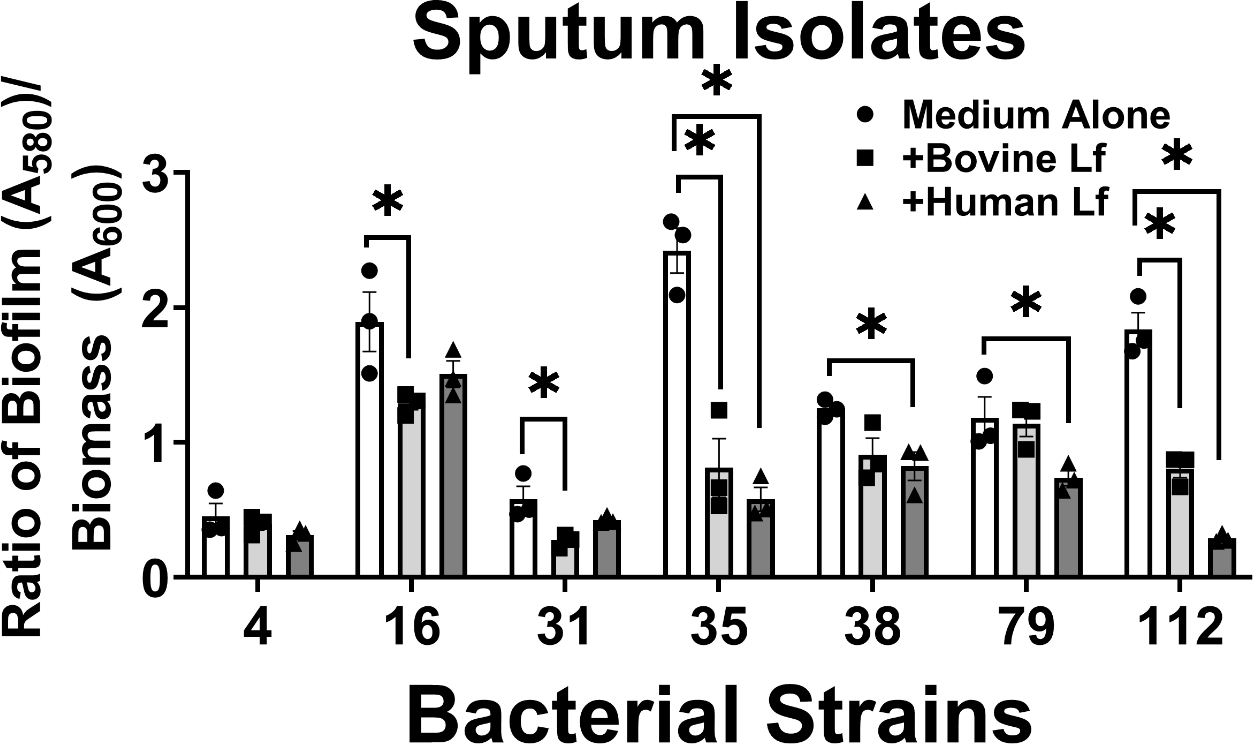
Analysis of the effect of bovine or human lactoferrin on biofilm formation by clinical strains of A. baumannii isolated from sputum (strains 4, 16, 31, 35, 38, 79, and 112). Bacterial biomass was measured at 24 hours post-inoculation by spectrophotometric measurement of optical density at 600 nm (OD600). Cultures were decanted, washed, and adherent biofilms were stained with crystal violet. Biofilm was quantified by solubilizing crystal violet in an 80%/20% ethanol: acetone solution and evaluation at 560 nm (OD560). Cultures were grown in medium alone (Medium Alone, designated by white bars and circle points) or medium supplemented with 125 μg/mL of either bovine lactoferrin (Bovine Lf, designated by light gray bars and square points) or human lactoferrin (Human Lf, designated by dark gray bars and triangle points). Points indicate individual experiments, bars indicate mean +/− SEM. Significant inhibition of bacterial biofilm compared to medium alone negative control was determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test, *P<0.05, n=3.
