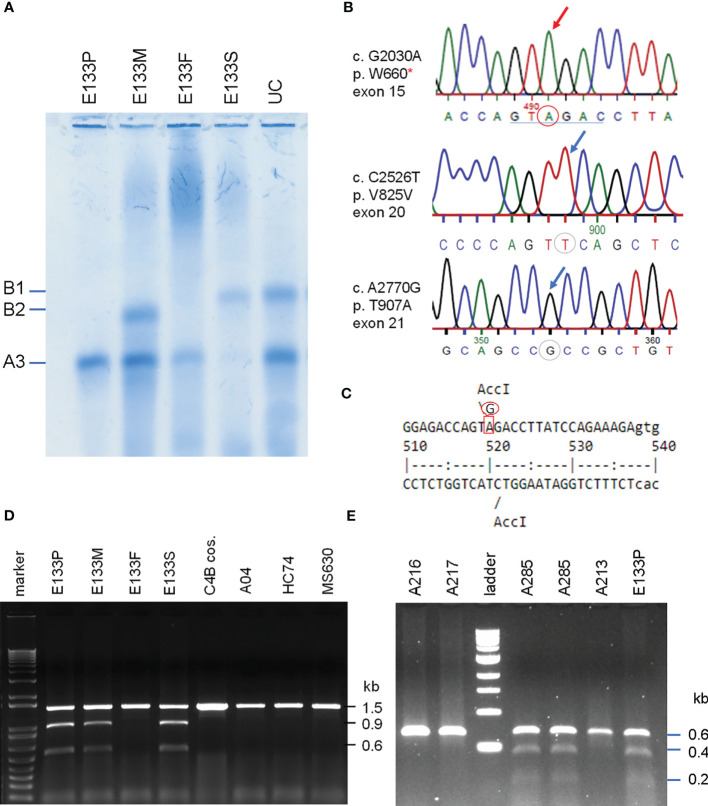
Figure 6.
Identification of the molecular defect leading to C4B deficiency in an Asian patient with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis (E133P). (A) Immunofixation of EDTA-plasma for C4 protein of the E133 patient (P), parents (M and F), and step-brother (S) plus an unrelated individual (UC). (B) Genomic DNA sequences showing conversion of W660 codon TGG conversion to nonsense codon TAG (W660x, upper). Middle and lower panels show two additional sequence variations for V825V from exon 20 (no change in amino acid) and for T907A from exon 21. (C) Genomic sequence that caused W660x mutation was distinguishable by AccI RFLP. (D) Analyses of the E133 family and control subjects. An 1.5 kb DNA fragment spanning between exon 14 to exon 18 from eight subjects were amplified by PCR, digested with restriction enzyme AccI and resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis. The results revealed that the W660x mutation was also present in his mother (E133M) and his stepbrother (E133S). (E) An improved method to detect W660x using a 0.6 kb fragment from intron 14 to intron 16 for AccI RFLP. Subject A285 was performed in duplicate to confirm the presence of W660x. The molecular weight marker was the kb-ladder. The GenBank accession number for the DNA fragment containing sequence with W660x from E133P is NZ203456.