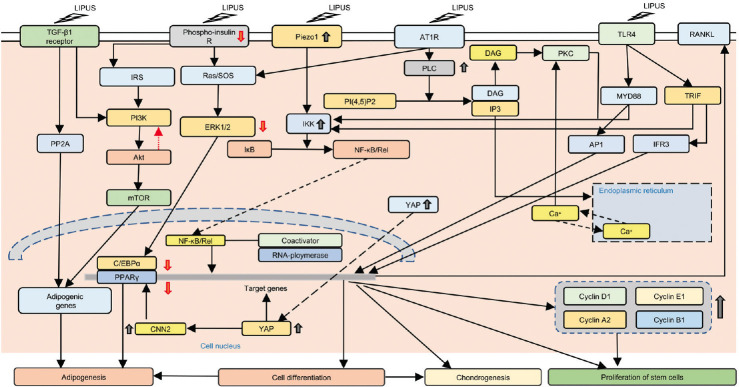
Figure 1.
LIPUS acts on stem cells through several signaling pathways. LIPUS can reduce the level of YAP phosphorylation, increase the active YAP in the cell, and promote the proliferation of C2C12 cells. LIPUS can promote the transfer of YAP to the nucleus of 3T3-L1 cells, resulting in the upregulation of CCN2 in the cells and reducing the expression of PPAR genes, which hinders the generation of mature fat cells. In addition, LIPUS reduces insulin signaling pathways by inhibiting insulin receptor phosphorylation, ERK1/2, and Akt, thereby inhibiting adipocyte differentiation. LIPUS can reduce the effect of the AT1-PLCβ pathway on the NF-κB translocation in the nucleus, while increasing the expression of Piezo1, activating the NF-κB signal through the piezoelectric 1-dependent pathway, increasing the expression of RANKL, promoting bone matrix formation, and enhancing osteogenesis. LIPUS can inhibit the activation of TLR4 channels by LPS and promote the expression of cyclin and the proliferation of hADMSCs. LIPUS: low-intensity pulsed ultrasound; AT1: angiotensin II type 1; AT1R: angiotensin II receptor type 1; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; RANKL: receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand; IRS: insulin receptor substrate; SOS: son of sevenless; PLC: phospholipase C; DAG: diacylglycerol; PKC: protein kinase C; MYD88: myeloid differentiation primary response 88; TRIF: TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β; IP3: inositol trisphosphate; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinases; Akt: protein kinase B; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinases; IKK: IκB kinase; PP2A: protein phosphatase 2; mTOR: mechanistic target of rapamycin; YAP: yes-associated protein; PPARγ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; CNN2: calponin 2; AP1: activator protein 1; IFR3: interferon regulatory factor 3; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B.