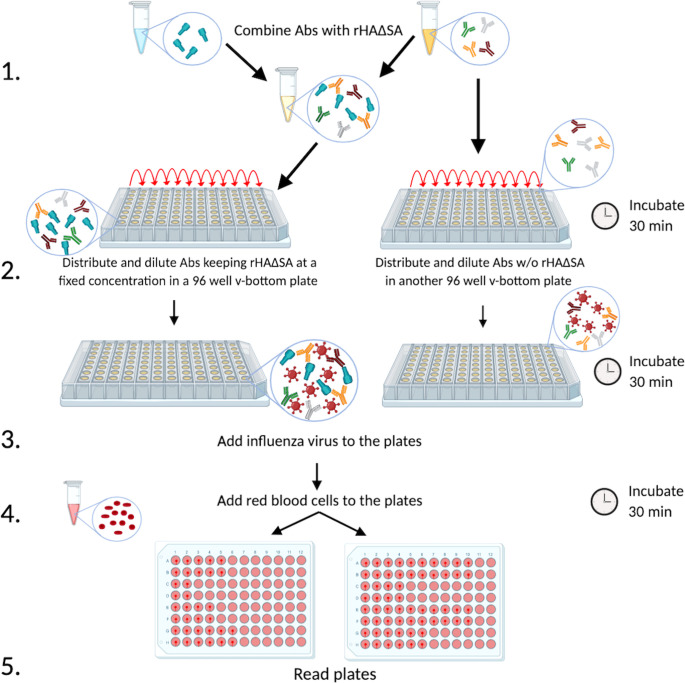
FIG 6.
Schematic representation of the R-HAI assay. Monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies from vaccinated or infected experimental animals or individuals are combined with rHAΔSA from a particular seasonal or pandemic influenza virus strain in order to absorb the antibodies specific to that HA (step 1). Subsequently, antibodies are distributed on a 96-well v-bottom plate in the presence or absence of HAΔSA (100 ng/well) (step 2), and the influenza virus of interest is added (step 3). Afterward, red blood cells are added (step 4), and the plates are read to determine HAI titer (step 5).