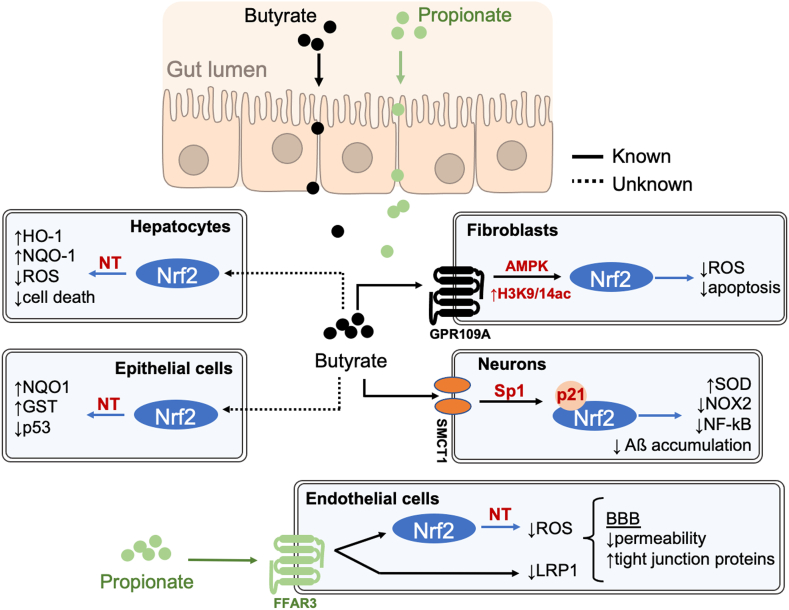
Fig. 4.
Schematic highlighting redox regulation by SCFAs in different cell types. Aβ: amyloid β peptide; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; BBB: blood-brain barrier; FFAR2: free fatty acid receptor 2; FFAR3: free fatty acid receptor 3; GR109A: G-protein-coupled receptor; GST: glutathione S-transferase; HDAC: histone deacetylase 1; HO1: heme oxygenase 1; H3K9/14 ac: histone H3 acetylated in lysine 9/14; iNOS: inducible nitric oxide synthase; LRP-1: LDL Receptor Related Protein 1; NF-kB: Nuclear factor kappa B; NO: nitric oxide; NOX2: NADPH oxidase 2; NQ1: NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase-1; Nrf2: nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2; NT: nuclear translocation; p21: p53: tumor suppressor p53; ROS: reactive oxygen species; SMCT1: sodium-coupled monocarboxylate transporter 1; SOD: superoxide dismutase; Sp1: specificity protein 1.