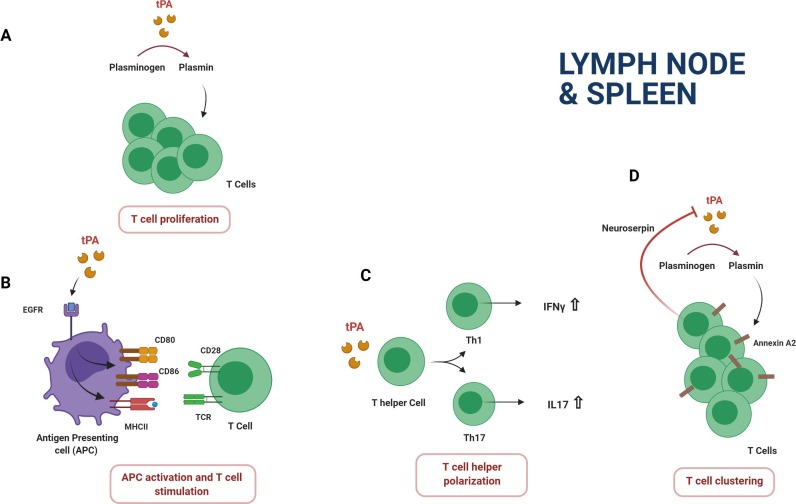
Fig. 2.
Effects of the plasminogen activation system on T cell functions. tPA increases MHC-II and costimulatory CD80 and CD86 molecule expression on antigen presenting cells (dendritic cells and macrophages) by the binding of the EGF-R. T cell activation and proliferation is enhanced by tPA through its proteolytic action (A). tPA increases the production of the proinflammatory cytokines IFN-γ and IL-17 (B). tPA contributes to the T cell clustering by a plasmin dependent mechanism. This effect is reversed by neuroserpin (C).