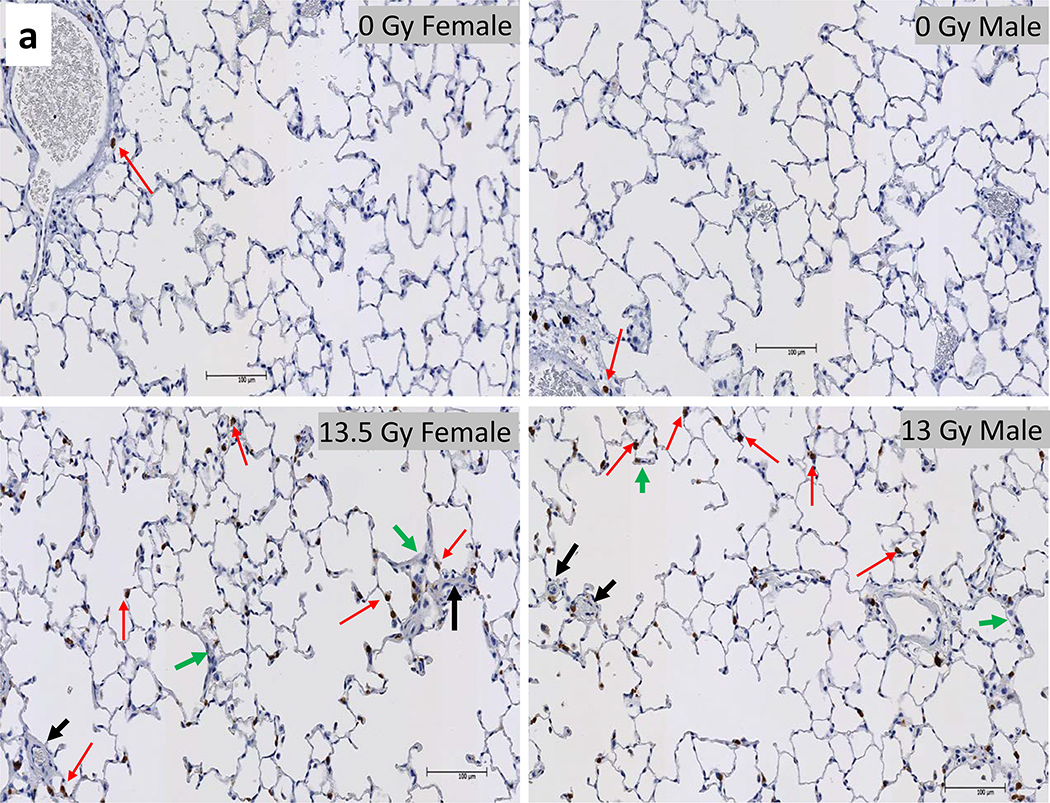
Figure 8a.
Histology of lung injury during pneumonitis. Irradiated female and male rats that were moribund between days 60–100 were accessed for radiation induced lung injury (RILI). Whole mount lung sections (4 μm thick) were stained with anti-tryptase antibody for mast cells (stained brown, red arrows).
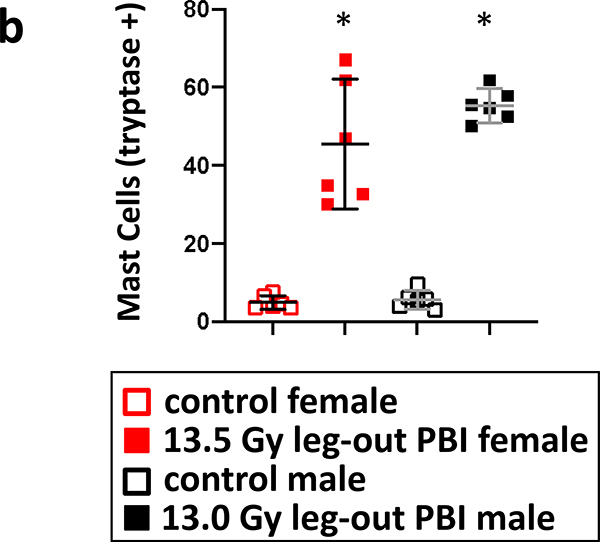
8b. Graphical representation of lung mast cell counts from female and male rats. Lungs from both female and male irradiated rats had increased numbers of mast cells compared to their sex-matched control rats. Nonirradiated control rat lungs were harvested at termination (150-day females and 180-day males) as no rats in these groups were moribund during pneumonitis. Data is presented as means and 95% CI. The asterisk (*) represents p<0.05 versus nonirradiated sex-matched rats.
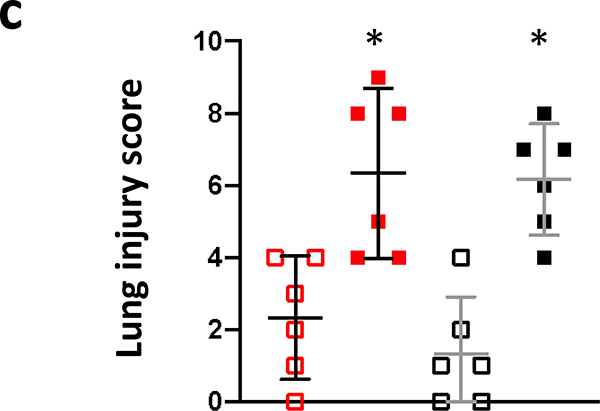
8c. Lung injury scores. Lung injury was scored as described in Materials and Methods. Individual scores for foamy macrophages, vascular wall thickness and alveolar wall thickness were determined on a 5-point scale as described (Medhora et al. 2014, 2015). A calculated mean composite lung injury score was derived and is shown. Data is presented as means and 95% CI. The asterisk (*) represents p<0.05 versus nonirradiated sex-matched rats.