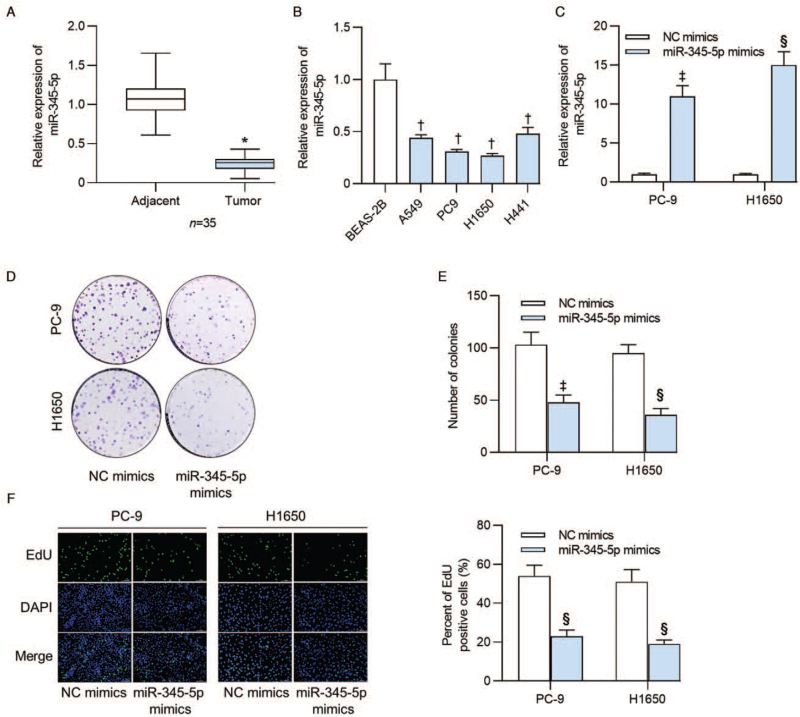
Figure 1.
MiR-345-5p expression displayed low levels in human lung adenocarcinoma tissues and cell lines and inhibited lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation. (A) RT-qPCR was conducted to examine the expression of miR-345-5p in 35 lung adenocarcinoma tissues and tumor adjacent tissues. (B) MiR-345-5p expression levels in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines (A549, PC9, H1650 and H441) and in normal human BEAS-2B were detected by RT-qPCR. (C) Expression of miR-345-5p in cells transfected with miR-345-5p mimics was assayed by RT-qPCR analysis. (D, E) Colony formation assay measured the effects of miR-345-5p overexpression on the number of colonies formed by PC-9 and H1650 cells. (F) Percent of EdU positive cells was determined by EdU assay in PC-9 and H1650 cells transfected with NC mimics or miR-345-5p mimics. ∗P < 0.001 vs. adjacent tissues; †P < 0.001 vs. BESA-2B; ‡P < 0.05, §P < 0.001 vs. NC mimics. BEAS-2B: Bronchial epithelium transformed with Ad12-SV40 2B; DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; EdU: 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine; miR-345-5p: MicroRNA-345-5p; NC: Negative control; RT-qPCR: Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction.