Fig. 4.
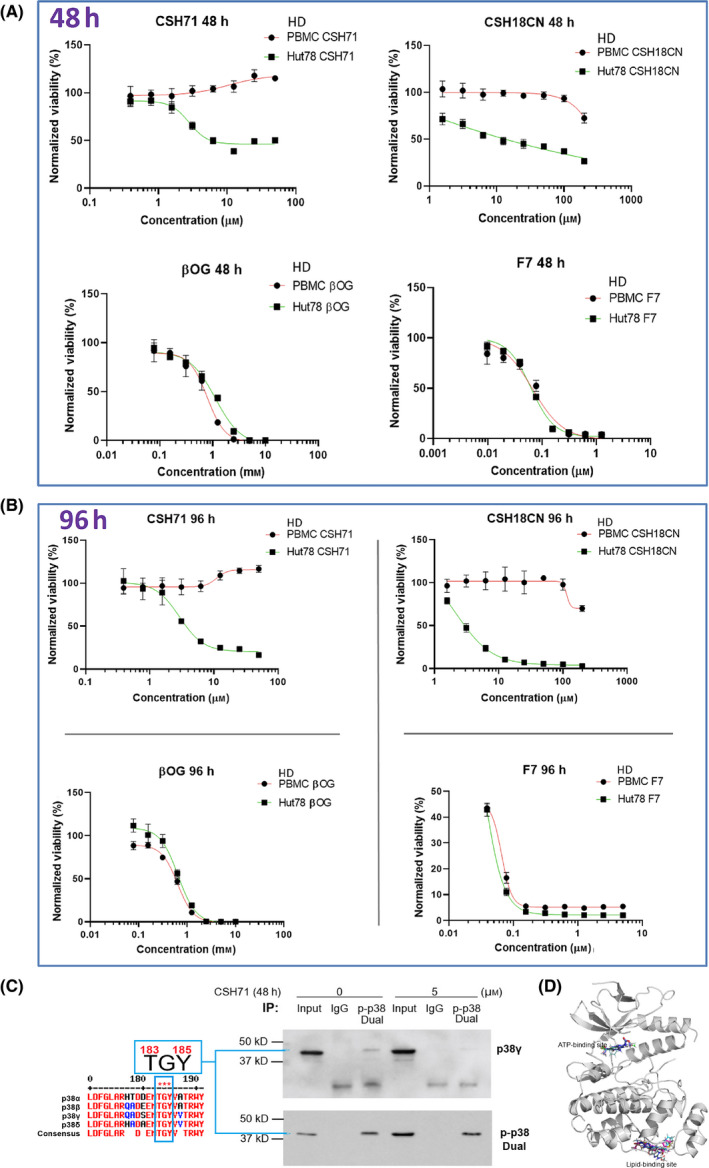
Cytotoxicity measurements of pure CSH71 and CSH18CN in CTCL cells. (A and B) Cytotoxicity assays and IC50s determination of newly synthesized compounds which are considered as two site binders CSH71 and CSH18CN Hut78 CTCL cells treated with increasing doses, respectively, for 48 h (A.) and 96 h. (B). F7 and β‐OG, served as one‐site binder, ATP binding and lipid‐binding of p38γ, respectively. PBMC from healthy donors (HD) used as a control as its p38γ level is at undetected level. Rest of text we focus on CSH71 for further analysis of its biological activity due to its interaction with the p38γ LBS. (C) Enrichment of dual‐phosphorylated p38 by Immunoprecipitation (IP). Sequence of p38 isoforms that all contain TGY motif dual activation site T180/183 GY182/185 (for p38γ the motif is T183‐G‐Y185, all other isoforms are T180 and Y182, Left). Right: IP results, first pulling down with dual‐p‐p38 of p38 antibody, then detect with p38γ and dual‐p p38 antibody, respectively, in cytosol of Hut78 cells both untreated (o µm) and CSH71‐treated (5 µm). The blue arrow points to p38γ that contains dual phosphorylation p‐p38 at T183‐G‐Y185. (D) CSH71 has only two predicted binding sites of p38γ by all around docking pose commutating analysis; and the MaxGScores of ATP‐binding and lipid‐binding, are −6.82, and −6.18 kcal·mol−1, respectively, which also indicates the binding affinity of CSH71 in LBD is much weaker than that of β‐OG with a MaxGScore of −8.9 kcal·mol−1.
