Fig. 5.
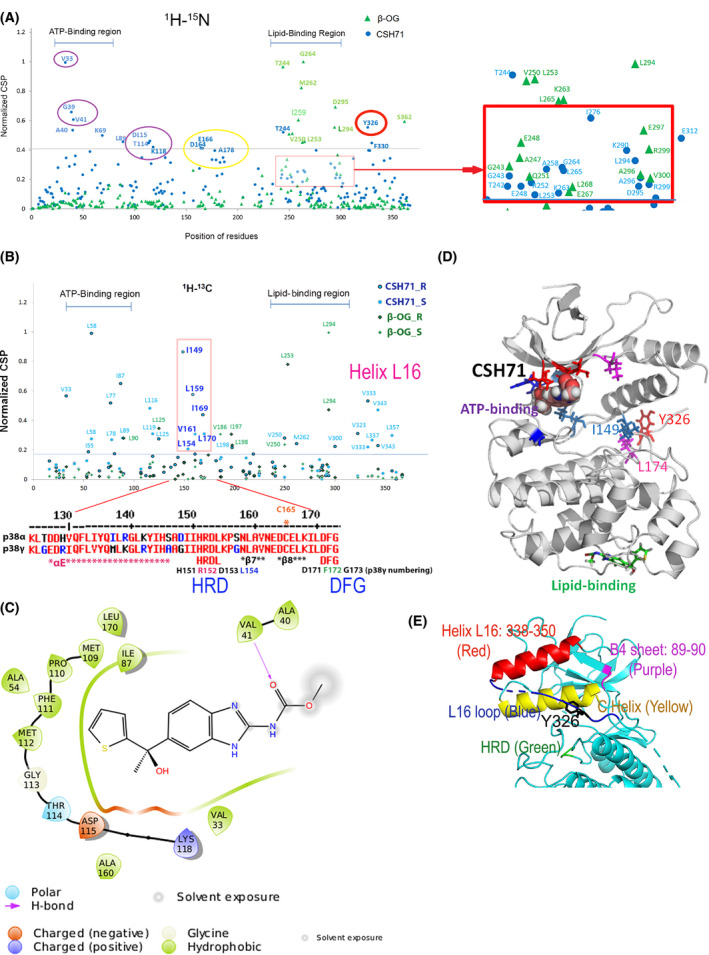
Compound CSH71 binds to two sites on p38γ in cell‐free based system. (A) NMR CSP 1H‐15N data for p38γ ‐ CSH71 (blue round dots) which prefers to bind to the ATP‐binding site, whereas β‐OG only binds to the lipid‐binding site (green triangles). The shifted residues V33, G39, V41, A40, and K69 (indicated by round blue dots, CSH71) are located at the ATP‐binding site of p38γ; red square showed the residues that CSH71 binds in the lipid‐binding domain significantly shifted are T244 (blue), I276 and E312. (B) NMR CSP the 1H‐13C HMQC spectra in the methyl region for p38γ showed HRD motif (151–153) and its adjacent residues (I149, L154, L159, V161, I169, and L170) highly disturbed in CSH71. It is consistent of others’ finding of p38a that pliable HRD folding of Helix L16 and L16 loop occurs upon compound binding of the LBD, which promotes trans‐auto phosphorylation via dimerization. (C) 2D interaction diagram of CSH71 in the ATP‐binding site of p38γ. V41 (Hydrogen bond); D115 (negative charged); and K118 (positive charged). Many hydrophobic are surrounding CSH71: V33, G39, and V41 on one side of the pocket; T114, D115, and K118 on the other side of the same pocket of p38γ. (D) Docking pose summarized NMR CSP 2D data of p38γ with CSH71, which shows how shifted C‐terminal residues that in Y326‐V348 segment (L16 loop and L16 helix) posit with those of are located in the ATP‐binding site. It is worth to note that along with two residues I149 and L174, Y326 of p38γ, a counterpart of the alternative phosphorylation site Y323 of p38α, in the interlobe region, may greatly shifted, making possible for opening up DEF pocket based on other’s studies (R. A. Engh [14] and O. Livnah [20]). (E) 3D structure of N‐terminal segments/domain of p38γ that contains residues that greatly shifted by CSH71. It illustrates a unique structure in the N‐lobe p38γ which contains an N‐terminal C Helix (yellow) that is sandwiched by C‐terminal sequences Helix L16 (red) and L16 loop (blue) where Y326 resides, the site for alternative phosphorylation by ZAP70. The conserved His‐Arg‐Asp (H151R152D153 motif, colored green), also greatly shifted and likely be protruding toward C Helix as binding of CSH71 to p38γ.
