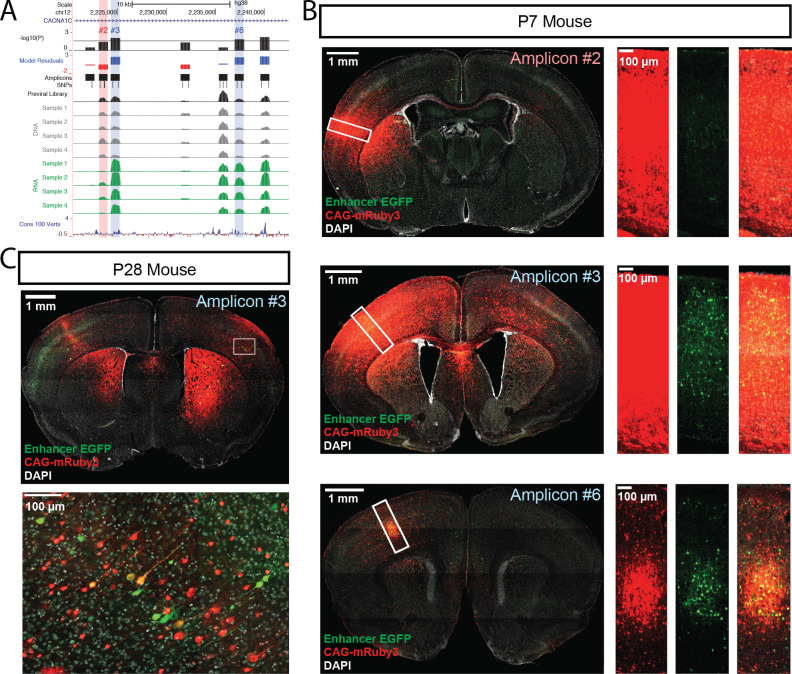
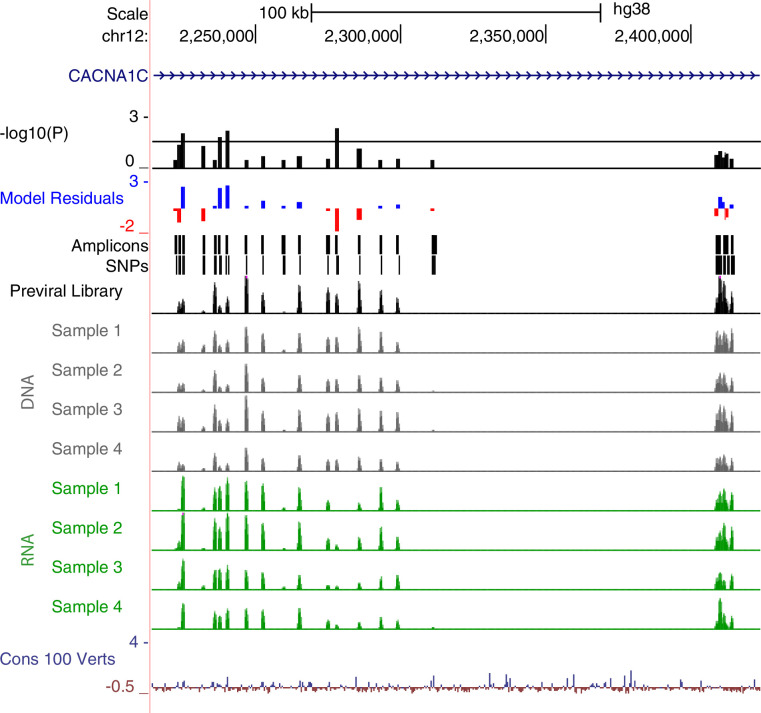
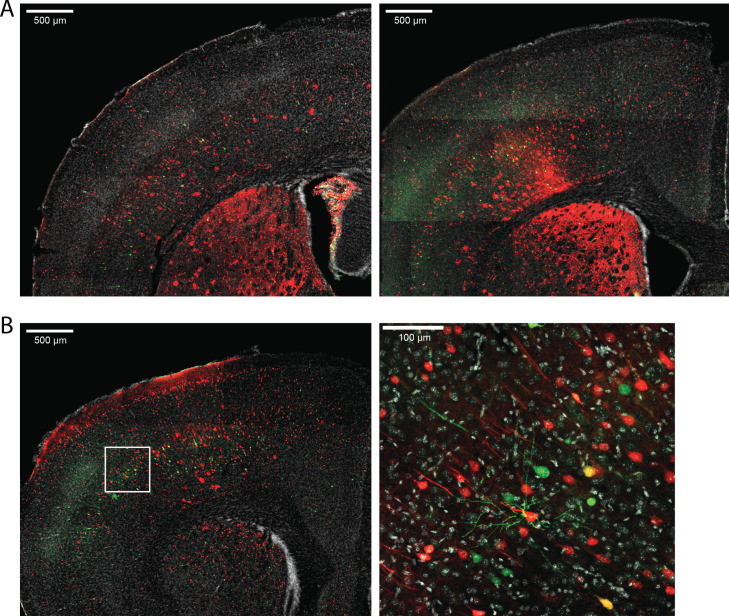
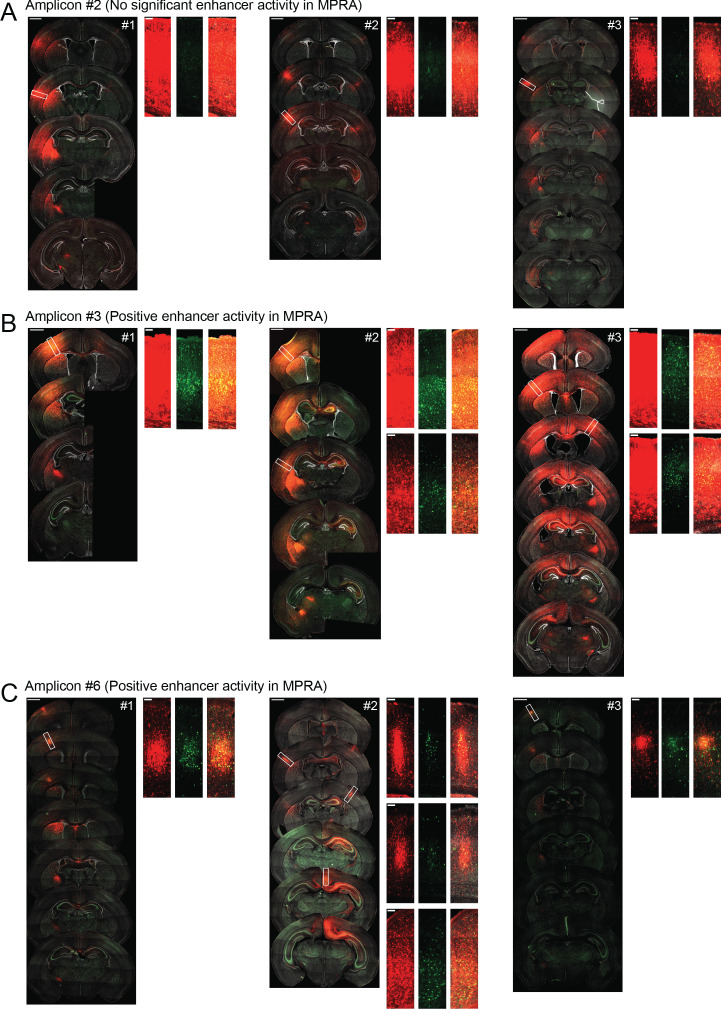
Figure 4. Functional dissection of the large third intron of CACNA1C.
(A) UCSC Genome Browser representation of amplicons #1 through #7 in the third intron of CACNA1C (hg38, chr12:2,220,500–2,242,499). UCSC tracks for GENCODE v36 and 100 vertebrate conservation, normalized coverage of aligned reads for the previral library, and DNA and RNA samples for the four biological replicates are shown; y-axis scale is 0–50,000 reads. MPRA analysis is shown as graphs of linear model residuals and -log10 transformed p-values. Three amplicons, #3, #6, and #7, were found significantly active in our assay. Amplicons which were tested in single-candidate experiments are highlighted (red for no activity in MPRA, blue for significant activity in MPRA) (B) Confocal images of single-candidate validation of amplicons #2, #3, and #6. Mice were transduced at P0 with two AAV vectors: one for an HspMinP-EGFP-3’-UTR enhancer reporter construct carrying the indicated amplicon and a second control vector, CAG-mRuby3. Brains were fixed at P7 and sectioned and stained with an antibody for EGFP for signal amplification. Tiled, whole section images are shown on the left. Closeup of boxed regions are shown in the panels on the right. Green, EGFP; red mRuby3; grey, DAPI. These experiments validated robust EGFP expression driven by the two positive MPRA hits (#3 and #6), with substantial EGFP reduction for the MPRA negative amplicon #2. (C) Mice were transduced with AAV including positive amplicon #3 and processed as in B, but were raised to P28 before fixing, sectioning, and staining.